A newly recognized multiple malformation syndrome with caudal regression associated with a biallelic c.402G>A variant in TBX4
- PMID: 31965066
- PMCID: PMC7170885
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-020-0572-5
A newly recognized multiple malformation syndrome with caudal regression associated with a biallelic c.402G>A variant in TBX4
Abstract
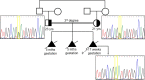
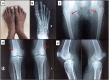
The T-box4 (TBX4) gene (OMIM *601719) belongs to the T-box family of transcription regulators that share a conserved homology domain and are expressed at specific sites during various stages of embryonic development. Tbx4 has been found to be a crucial transcriptional regulator in embryonic hindlimb development in animal models. Monoallelic variants in the TBX4 gene are reported to be associated with skeletal defects of the pelvis and lower limbs. We report here a fetus with a novel multiple malformation syndrome associated with sacrococcygeal agenesis, bilateral lower limb aplasia, hypoplastic left heart, bilateral lung hypoplasia, hydroureteronephrosis, and nonimmune fetal hydrops, found to have a homozygous nonsense variant in the TBX4 gene. We propose that biallelic variants in the TBX4 gene are associated with a severe syndromic phenotype of sacrococcygeal agenesis and lower limb reduction defects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Horton AC, Mahadevan NR, Minguillon C, Osoegawa K, Rokhsar DS, Ruvinsky I, et al. Conservation of linkage and evolution of developmental function within the Tbx2/3/4/5 subfamily of T-box genes: implications for the origin of vertebrate limbs. Dev Genes Evol. 2008;218:613–28. doi: 10.1007/s00427-008-0249-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

