Mechanisms underlying the protective effects of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy
- PMID: 31965214
- PMCID: PMC7223321
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03454-6
Mechanisms underlying the protective effects of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy
Abstract
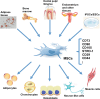
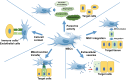
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been extensively investigated for the treatment of various diseases. The therapeutic potential of MSCs is attributed to complex cellular and molecular mechanisms of action including differentiation into multiple cell lineages and regulation of immune responses via immunomodulation. The plasticity of MSCs in immunomodulation allow these cells to exert different immune effects depending on different diseases. Understanding the biology of MSCs and their role in treatment is critical to determine their potential for various therapeutic applications and for the development of MSC-based regenerative medicine. This review summarizes the recent progress of particular mechanisms underlying the tissue regenerative properties and immunomodulatory effects of MSCs. We focused on discussing the functional roles of paracrine activities, direct cell-cell contact, mitochondrial transfer, and extracellular vesicles related to MSC-mediated effects on immune cell responses, cell survival, and regeneration. This will provide an overview of the current research on the rapid development of MSC-based therapies.
Keywords: Cell–cell contact; Extracellular vesicles; Immunomodulation; Integration of MSCs; Mitochondrial transfer; Regenerative potential; Soluble factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Piatetzky S, II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966;16(3):381–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

