Hardware removal rates after surgical treatment of proximal femur fractures : Nationwide trends in Finland in 1997-2016
- PMID: 31965281
- PMCID: PMC7351871
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-020-03356-z
Hardware removal rates after surgical treatment of proximal femur fractures : Nationwide trends in Finland in 1997-2016
Abstract
Background: Various internal fixation methods have been used to treat proximal femur fractures and occasionally the fixation material is removed. However, nationwide trends of hardware removals are not known. Thus, this study investigated the hardware removal rates after proximal femur fractures in Finland during 1997-2016.
Materials and methods: Finnish adults aged 18 years or older in 1997-2016 formed the basic study population. From the National Hospital Discharge Register patients with trochanteric femur fracture treated with an intramedullary nail (IMN) or dynamic hip screw (DHS), and patients with femoral neck fracture treated with screw fixation, were included. Hardware removal and secondary prosthesis rates were assessed.
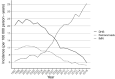
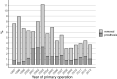
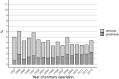
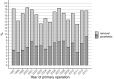
Results: Altogether 41,253 patients underwent proximal femoral fracture fixation surgery in Finland in 1997-2016. Of these, 16,152 were DHS surgery and 15,724 IMN surgery and 8491 underwent screw operation of femoral neck fracture. The total removal rates of DHS and IMN were 5.5% and 5.4%. The total removal rate of screw fixations of the femoral neck was higher, 18.5%. The total removal rates during the first 3 years after the IMN more than halved in 1997-2013, from 7.6% to 3.7%, whereas the removal rate of the DHS or screw fixation of femoral neck fractures did not show consistent trend. The rate of secondary prosthesis operations following DHS and IMN was low (1.8% for both). This was in clear contrast to the prosthesis rate following screw fixations of the femoral neck (7.2%).
Conclusions: IMN operations largely replaced DHS operations in trochanteric fractures of the proximal femur in Finland in 1997-2016. The removal and secondary prosthesis rates of the DHS and IMN were clearly lower than the corresponding rates after screw fixations of the femoral neck fracture.
Level of evidence: III, Epidemiologic study.
Keywords: Endoprosthesis; Fixation; Material; Removal; Secondary.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dynamic hip screw fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021 Oct;31(7):1435-1441. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-02895-4. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021. PMID: 33590318 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion to total hip arthroplasty after failed proximal femoral nail antirotations or dynamic hip screw fixations for stable intertrochanteric femur fractures: a retrospective study with a minimum follow-up of 3 years.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Jan 25;18(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1415-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28122548 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation Vs. Proximal Femur Nail For Unstable Per-Trochanteric Fractures: A Comparative Analysis Of Outcomes And Complications.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2021 Jan-Mar;33(1):34-38. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2021. PMID: 33774951
-
Is the increased use of intramedullary nailing over DHS for intertrochanteric hip fractures justified? - A review of the Irish hip fracture database 2016 -2020.Surgeon. 2024 Feb;22(1):31-36. doi: 10.1016/j.surge.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Surgeon. 2024. PMID: 37793947 Review.
-
Subtrochanteric femur fracture after removal of screws for femoral neck fracture in a child.Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015 Jan;44(1):40-2. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015. PMID: 25566556 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of risk factors for difficult implant removal in children with slipped capital femoral epiphysis treated by cannulated screws.Front Pediatr. 2024 May 22;12:1414557. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1414557. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38840800 Free PMC article.
-
Lag Screw Exchange for Impinging Lateral Hardware Following Intramedullary Nailing of Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures - A Case Series Demonstrating Efficacy.Iowa Orthop J. 2024;44(1):167-171. Iowa Orthop J. 2024. PMID: 38919366 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and radiological results of using proximal femoral locking compression plate and proximal femoral nail antirotation for subtrochanteric fractures.Eur J Transl Myol. 2022 May 12;32(2):10422. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2022.10422. Eur J Transl Myol. 2022. PMID: 35546727 Free PMC article.
-
Revision rate of displaced femoral neck fractures in non-elderly adults: a retrospective comparative study of the femoral neck system and cannulated screws.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Sep 16;19(1):571. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05056-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39285432 Free PMC article.
-
Pinloc or Hansson pins: a multicenter, randomized controlled study of 439 patients treated for femoral neck fractures.OTA Int. 2023 Sep 22;6(4):e282. doi: 10.1097/OI9.0000000000000282. eCollection 2023 Dec. OTA Int. 2023. PMID: 37744995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams CI, Robinson CM, McQueen MM. Prospective randomized controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus dynamic screw and plate for intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(6):394–400. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari M, Devereaux P, Swiontkowski MF, et al. Internal fixation compared with arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck: a meta-analysis. JBJS. 2003;85(9):1673–1681. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari M, Schemitsch E, Jönsson A, Zlowodzki M, Haidukewych GJ. Gamma nails revisited: gamma nails versus compression hip screws in the management of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6):460–464. - PubMed
-
- Bienkowski P, Reindl R, Berry GK, Iakoub E, Harvey EJ. A new intramedullary nail device for the treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures: Perioperative experience. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2006;61(6):1458–1462. - PubMed
-
- Black J. Does corrosion matter? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70(4):517–520. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

