Origin of RNA Polymerase II pause in eumetazoans: Insights from Hydra
- PMID: 31965986
- PMCID: PMC7212077
- DOI: 10.1007/s12038-019-9979-y
Origin of RNA Polymerase II pause in eumetazoans: Insights from Hydra
Abstract
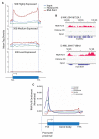
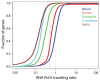
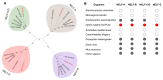
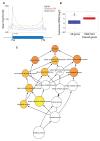
Multicellular organisms have evolved sophisticated mechanisms for responding to various developmental, environmental and physical stimuli by regulating transcription. The correlation of distribution of RNA Polymerase II (RNA Pol II) with transcription is well established in higher metazoans, however genome-wide information about its distribution in early metazoans, such as Hydra, is virtually absent. To gain insights into RNA Pol II-mediated transcription and chromatin organization in Hydra, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-coupled high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq) for RNA Pol II and Histone H3. Strikingly, we found that Hydra RNA Pol II is uniformly distributed across the entire gene body, as opposed to its counterparts in bilaterians such as human and mouse. Furthermore, correlation with transcriptome data revealed that the levels of RNA Pol II correlate with the magnitude of gene expression. Strikingly, the characteristic peak of RNA Pol II pause typically observed in bilaterians at the transcription start sites (TSSs) was not observed in Hydra. The RNA Pol II traversing ratio in Hydra was found to be intermediate to yeast and bilaterians. The search for factors involved in RNA Pol II pause revealed that RNA Pol II pausing machinery was most likely acquired first in Cnidaria. However, only a small subset of genes exhibited the promoter proximal RNP Pol II pause. Interestingly, the nucleosome occupancy is highest over the subset of paused genes as compared to total Hydra genes, which is another indication of paused RNA Pol II at these genes. Thus, this study provides evidence for the molecular basis of RNA Pol II pause early during the evolution of multicellular organisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of promoter-proximal RNA polymerase II pausing across mammalian cell types.Genome Biol. 2016 Jun 3;17(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-0984-2. Genome Biol. 2016. PMID: 27259512 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II pausing downstream of core histone genes is different from genes producing polyadenylated transcripts.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038769. Epub 2012 Jun 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22701709 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Pol II Pausing Is Involved in Daily Gene Transcription in the Mouse Liver.J Biol Rhythms. 2018 Aug;33(4):350-362. doi: 10.1177/0748730418779526. Epub 2018 May 30. J Biol Rhythms. 2018. PMID: 29845885
-
Promoter proximal pausing on genes in metazoans.Chromosoma. 2009 Feb;118(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00412-008-0182-4. Epub 2008 Oct 2. Chromosoma. 2009. PMID: 18830703 Review.
-
Ready, pause, go: regulation of RNA polymerase II pausing and release by cellular signaling pathways.Trends Biochem Sci. 2015 Sep;40(9):516-25. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015. PMID: 26254229 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The NELF pausing checkpoint mediates the functional divergence of Cdk9.Nat Commun. 2023 May 13;14(1):2762. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38359-y. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37179384 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation in Hydra: Conserved and Divergent Roles.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 10;9:663208. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.663208. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34041242 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bosch TC. Why polyps regenerate and we don’t: towards a cellular and molecular framework for Hydra regeneration. Dev Biol. 2007;303:421–433. - PubMed
-
- Bosch TC. What Hydra has to say about the role and origin of symbiotic interactions. Biol Bull. 2012;223:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Broun M, Gee L, Reinhardt B, Bode HR. Formation of the head organizer in hydra involves the canonical Wnt pathway. Development. 2005;132:2907–2916. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
