Glycine protects against non-alcoholic hepatitis by downregulation of the TLR4 signaling pathway
- PMID: 31966360
- PMCID: PMC6965812
Glycine protects against non-alcoholic hepatitis by downregulation of the TLR4 signaling pathway
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of glycine on regulation of the hepatic toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway by metabolic endotoxemia in a rat model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
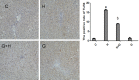
Methods: The NASH rat model was generated by feeding the animals a high-sucrose, high-fat for diet for 12 weeks. We then measured alterations in levels of LPS, TNFα, IL-6, ALT, TG in plasma, and TNFα, and IL-6 in liver. We performed hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and immunohistochemical staining to document pathological changes. Expression of TLR4 and IRS-1 in liver was measured by Western Blot and RT-PCR.
Results: Compared with control animals, levels of LPS, TNFα, IL-6 in plasma and the levels of TNFα, IL-6 in liver tissues gradually increased. Pathological changes and expression of TLR4 in liver were significantly increased compared with control. mRNA and protein levels of TLR4 and IRS-1 in livers were also upregulated. With concomitant treatment with glycine, endotoxin levels decreased, and TNFα and IL-6 levels in plasma and liver were significantly decreased compared to NASH rats. Pathological changes in liver and immunohistological expression of TLR4 in liver tissues were significantly improved compared to NASH rats. mRNA and protein levels of TLR4 were significantly downregulated while mRNA and protein levels of IRS-1 in liver were markedly upregulated. Progression of NASH appeared to be slowed or limited.
Conclusion: These data suggest that hepatic TLR4 signaling pathway is activated in the NASH rat, and oral glycine may reduce the risk of endotoxemia and inflammation of the liver.
Keywords: Glycine; intestinal endotoxin; non-alcoholic steatoheptitis; type 4 toll-like receptors.
IJCEP Copyright © 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of Soothing Gan (Liver) and Invigorating Pi (Spleen) Recipes on TLR4-p38 MAPK Pathway in Kupffer Cells of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Rats.Chin J Integr Med. 2019 Mar;25(3):216-224. doi: 10.1007/s11655-018-2829-6. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Chin J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 29335857
-
Glycine protects against high sucrose and high fat-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80223-80237. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12831. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27784003 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Trefoil Factor 3 Alleviates the Intestinal Barrier Function Through Reducing the Expression of TLR4 in Rats with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Arch Med Res. 2019 Jan;50(1):2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2019.03.004. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Arch Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31101239
-
Green tea extract treatment reduces NFκB activation in mice with diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by lowering TNFR1 and TLR4 expression and ligand availability.J Nutr Biochem. 2017 Mar;41:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.12.007. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Nutr Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28038359
-
1,25(OH)2D3 downregulates the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory pathway and ameliorates liver injury in diabetic rats.J Endocrinol Invest. 2015 Oct;38(10):1083-91. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0287-6. Epub 2015 Apr 24. J Endocrinol Invest. 2015. PMID: 25906757 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Untargeted metabonomics and TLR4/ NF-κB signaling pathway analysis reveals potential mechanism of action of Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 3;15:1374158. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1374158. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38887554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization WH. Obesity and overweight fact sheet. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012. p. 311.
-
- Smith BW, Adams LA. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2011;48:97–113. - PubMed
-
- Argo CK, Northup PG, Al-Osaimi AM, Caldwell SH. Systematic review of risk factors for fibrosis progression in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2009;51:371–9. - PubMed
-
- Köroğlu E, Canbakan B, Atay K, Hatemi İ, Tuncer M, Dobrucalı A, Sonsuz A, Gültepe I, Şentürk H. Role of oxidative stress and insulin resistance in disease severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2016;27:361–366. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
