microRNA-802 is involved in palmitate-induced damage to pancreatic β cells through repression of sirtuin 6
- PMID: 31966484
- PMCID: PMC6965834
microRNA-802 is involved in palmitate-induced damage to pancreatic β cells through repression of sirtuin 6
Abstract
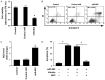
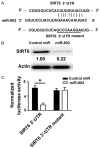
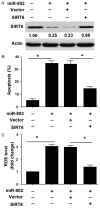
Free fatty acid (FFA)-induced pancreatic β-cell loss is implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). It has been documented that circulating microRNA (miR)-802 levels are significantly greater in T2DM patients than in healthy subjects. However, the role of miR-802 in FFA-induced damage to β cells is still unclear. In the present study, we measured the expression of miR-802 in the INS-1 rat insulinoma cell line after palmitate treatment for 48 h. Gain- and loss-of-function studies were conducted to determine the function of miR-802 in palmitate-induced apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. The target gene(s) of miR-802 was functionally characterized. Compared to control cells, palmitate treatment caused a time- and concentration-dependent induction of miR-802 in INS-1 cells. Knockdown of miR-802 significantly blocked palmitate-induced apoptosis and attenuated ROS formation. Moreover, miR-802 downregulation prevented the reduction of prosurvival proteins Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL by palmitate. In contrast, ectopic expression of miR-802 stimulated apoptosis and ROS generation in INS-1 cells. Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) was identified to be a direct target gene of miR-802. Overexpression of miR-802 suppressed the expression of SIRT6. Enforced expression of SIRT6 abolished the induction of apoptosis and ROS production by miR-802. Taken together, miR-802 is required for palmitate-induced damage to β cells by targeting SIRT6 and represents a potential therapeutic target for T2DM.
Keywords: Diabetes; SIRT6; free fatty acid; miR-802.
IJCEP Copyright © 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Khodabandehloo H, Gorgani-Firuzjaee S, Panahi G, Meshkani R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Transl Res. 2016;167:228–256. - PubMed
-
- Wilding JP. The importance of free fatty acids in the development of Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2007;24:934–945. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Cui C, Nie A, Wang Y, Ni Q, Liu Y, Yin Q, Zhang H, Li Y, Wang Q, Gu Y, Ning G. The mTORC2/PKC pathway sustains compensatory insulin secretion of pancreatic β cells in response to metabolic stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1861:2039–2047. - PubMed
-
- Cassel R, Ducreux S, Alam MR, Dingreville F, Berlé C, Burda-Jacob K, Chauvin MA, Chikh K, Païta L, Al-Mawla R, Crola Da Silva C, Rieusset J, Thivolet C, Van Coppenolle F, Madec AM. Protection of human pancreatic islets from lipotoxicity by modulation of the translocon. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0148686. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
