The diagnostic and prognostic value of serum miR-206 in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 31966596
- PMCID: PMC6965214
The diagnostic and prognostic value of serum miR-206 in colorectal cancer
Abstract
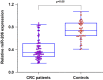
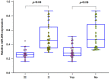
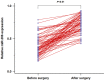
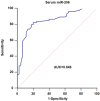
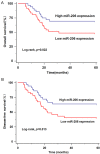
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) are emerging as promising biomarkers for colorectal cancer (CRC). In this study, we sought to examine the diagnostic and prognostic role of serum miR-206 in CRC. A total of 73 CRC cases and 45 healthy control subjects were enrolled in this study. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to measure the relative serum miR-206 levels. Serum miR-206 levels were significantly decreased in CRC patients than normal controls. In addition, serum miR-206 demonstrated good diagnostic performance for discriminating CRC patients from healthy controls. miR-206 levels were increased in the blood samples of CRC patients who received surgery treatment. Moreover, serum miR-206 expression was closely associated with TNM stage and lymph node metastasis. CRC patients with low miR-206 level suffered more unfavorable overall survival and disease free survival compared to those with high miR-206 level. Furthermore, serum miR-206 was confirmed to be an independent prognostic indicator for CRC. In summary, serum miR-206 might be a promising biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of CRC.
Keywords: Serum miR-206; biomarker; colorectal cancer; diagnosis; prognosis.
IJCEP Copyright © 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical response and prognostic significance of serum miR-497 expression in colorectal cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2019;25(1):11-18. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181902. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 31006664
-
Prognostic significance of serum miR-193b in colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Sep 1;10(9):9509-9514. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966826 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated serum miR-675 predicts poor prognosis for colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Jul 1;10(7):8043-8049. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966656 Free PMC article.
-
Serum microRNAs: A new diagnostic method for colorectal cancer.Biomed Rep. 2013 Jul;1(4):495-498. doi: 10.3892/br.2013.109. Epub 2013 May 20. Biomed Rep. 2013. PMID: 24648974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA as Diagnostic Biomarkers in Early Colorectal Cancer-A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 23;12(1):52. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010052. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31878015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-206 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the c-Met/AKT/GSK-3β pathway.Oncol Lett. 2021 Feb;21(2):147. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12408. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33633805 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in microRNAs as Emerging Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer Early Detection and Diagnosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 15;25(20):11060. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011060. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of Serum miR-133b and miR-206 Associate with Clinical Outcomes of Progression as Monitoring Biomarkers for Metastasis Colorectal Cancer Patients.Microrna. 2024;13(1):56-62. doi: 10.2174/0122115366266024240101075745. Microrna. 2024. PMID: 38231064 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value and Clinicopathological Features of MicroRNA-206 in Various Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 20;2020:2159704. doi: 10.1155/2020/2159704. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33145343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glimepiride Compared to Liraglutide Increases Plasma Levels of miR-206, miR-182-5p, and miR-766-3p in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Diabetes Metab J. 2023 Sep;47(5):668-681. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0342. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Diabetes Metab J. 2023. PMID: 37349083 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Zheng ZX, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Chen WQ. Colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2010. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:8455–8460. - PubMed
-
- Walsh JM, Terdiman JP. Colorectal cancer screening: scientific review. JAMA. 2003;289:1288–1296. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
