MicroRNA-3941 targets IGF-1 to regulate cell proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells
- PMID: 31966610
- PMCID: PMC6965230
MicroRNA-3941 targets IGF-1 to regulate cell proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells
Abstract
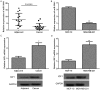
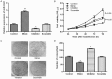
We aimed to investigate the effects and regulatory mechanism of microRNA-3941 (miR-3941) in the progression of breast cancer. The expression of miR-3941 and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) was determined in breast cancer tissues and cell lines. A miR-3941 mimics, inhibitor, and scramble RNA were individually transfected into the cancer cells. Then, the effects of overexpression and suppression of miR-3941 on cell viability, migration, and invasion, as well as on the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins (E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin) were further investigated. In addition, luciferase reporter analysis was performed to confirm whether IGF-1 was the potential target of miR-3941. Small interfering RNA targeting IGF-1 was transfected into the cells to further investigate whether miR-3941 regulated the breast cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting IGF-1. The inverse expression of miR-3941 (downregulated) and IGF-1 (upregulated) was observed in the breast cancer tissues and cells. The overexpression of miR-3941 significantly inhibited the breast cancer cell viability and suppressed cell migration and invasion. In addition, IGF-1 was confirmed as the target of miR-3941, and IGF-1 expression was negatively regulated by miR-3941. The knockdown of IGF-1 significantly reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-3941 overexpression on cell migration, invasion, and the EMT-related proteins. Our results indicate that miR-3941 is downregulated in breast cancer cells, and the downregulation of miR-3941 may promote breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through not targeting IGF-1 expression. miR-3941 and IGF-1 may serve as diagnostic markers or potential targets for breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; cell invasion; cell migration; cell proliferation; insulin-like growth factor 1; microRNA-3941.
IJCEP Copyright © 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
miR-448 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells by directly targeting the E-cadherin repressor ZEB1/2.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Mar;243(5):473-480. doi: 10.1177/1535370218754848. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 29368542 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase GCNT3 by miR-302b-3p Decreases Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3):987-1004. doi: 10.1159/000494482. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30355927
-
MiR-410 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Cells by Directly Targeting ERLIN2 via the ERS Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(2):461-474. doi: 10.1159/000491777. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30016800
-
MicroRNA-183 in Cancer Progression.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;11(6):1315-1324. doi: 10.7150/jca.39044. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32047538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relevance of miR-223 as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers in Cancer.Biology (Basel). 2022 Feb 6;11(2):249. doi: 10.3390/biology11020249. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Interplay Between Non-coding RNAs and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Neoplasia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 9;9:634512. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.634512. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33768092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-29a-3p mitigates the development of osteosarcoma through modulating IGF1 mediated PI3k/Akt/FOXO3 pathway by activating autophagy.Cell Cycle. 2022 Sep;21(18):1980-1995. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2078614. Epub 2022 May 31. Cell Cycle. 2022. PMID: 35575588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mothobi MN, editor. Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths among women. 2013. https://www.lap-publishing.com/
-
- World Health Organization. World Cancer Report. 2014
-
- Stebbing J, Slater S, Slevin M. Breast cancer (metastatic) Clin Evid. 2006;15:2331–2359. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
