High expression of NME1 correlates with progression and poor prognosis in patients of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 31966710
- PMCID: PMC6965413
High expression of NME1 correlates with progression and poor prognosis in patients of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
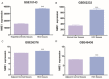
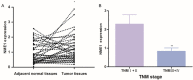
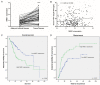
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies that results from genes regulation via different pathways. NME/NM23 nucleoside diphosphate kinase 1 (NME1) is generally regarded as a metastasis suppressor, but its function in HCC is largely unknown. In our study, we explored the role of NME1 in HCC. By analyzing the gene expression omnibus (GEO) database, we discovered that NME1 was more highly expressed in HCC tumor tissues than non-HCC liver tissues (P < 0.001), and NME1 was significantly up-regulated in HCC tumor tissues than in adjacent normal tissues (P < 0.001). Then, validated by the enrolled HCC patients and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, NME1 was upregulated in HCC tumor tissues compared with matched adjacent normal tissue (P < 0.05). Besides, NME1 was down-regulated in Stage III/IV HCC patients than Stage I/II HCC patients (P = 0.009). Moreover, Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that HCC patients with high NME1 expression had poor overall survival (P = 0.004) and higher recurrence rate (P < 0.001). Our data revealed that NME1 was a special oncogene, and its expression was significantly associated with the progression and prognosis of HCC. NME1 may be a novel molecular biomarker for the targeted therapy and prognosis of HCC.
Keywords: NME1; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis.
IJCEP Copyright © 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RPL19 Is a Prognostic Biomarker and Promotes Tumor Progression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 19;9:686547. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.686547. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34350180 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of the tumour suppressor κ-opioid receptor predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2017 Aug 18;17(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3541-9. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28821282 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and significance of heparanase and nm23-H1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Mar 7;11(9):1378-81. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i9.1378. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15761980 Free PMC article.
-
Learning about the functions of NME/NM23: lessons from knockout mice to silencing strategies.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;384(4-5):421-31. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0649-3. Epub 2011 May 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21562815 Review.
-
Nuclear functions of NME proteins.Lab Invest. 2018 Feb;98(2):211-218. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2017.109. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Lab Invest. 2018. PMID: 29058704 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metastasis suppressor genes in clinical practice: are they druggable?Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Dec;42(4):1169-1188. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10135-w. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37749308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Graph Models to the Identification of Transcriptomic Oncometabolic Pathways in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 3;14(6):653. doi: 10.3390/biom14060653. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38927057 Free PMC article.
-
The first central precocious puberty proteomic profiles revealed multiple metabolic networks and novel key disease-associated proteins.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Nov 8;13(21):24236-24250. doi: 10.18632/aging.203676. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34748517 Free PMC article.
-
[Roles of Histidine Kinases and Histidine Phosphatases in Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021 Sep 20;24(9):646-652. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2021.102.28. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34455734 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Hsa_circ_ROBO1 competes with miR-324-3p and upregulates NME1 to promote tumor metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;15(1):398. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01220-9. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39222250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–386. - PubMed
-
- Zucman-Rossi J, Villanueva A, Nault JC, Llovet JM. Genetic landscape and biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1226–1239. e1224. - PubMed
-
- Nahon P, Zucman-Rossi J. Single nucleotidepolymorphisms and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2012;57:663–674. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
