Utility of genetic variants to predict prognosis in coronary artery disease patients receiving statin treatment
- PMID: 31966745
- PMCID: PMC6965393
Utility of genetic variants to predict prognosis in coronary artery disease patients receiving statin treatment
Abstract
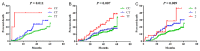
Statins are widely used drugs for lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and can prevent cardiovascular events. This study aimed to evaluate the influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and their cumulative effects on the prognosis of coronary artery disease (CAD) patients treated with statins. Sixteen SNPs were genotyped in 785 CAD patients receiving statin therapy, and their associations with clinical features and prognosis of patients were investigated. Four SNPs (rs2296651, rs11206510, rs8192870, and rs1801133) were significantly associated with complications of CAD (P<0.05). Four SNPs (rs8192870, rs4149056, rs12916, and rs2231142) affected blood lipid levels (P<0.05). Furthermore, rs1801133 showed a weak but significant association with fasting plasma glucose (P = 0.033). Survival analyses showed that rs11206510 (adjusted HR = 1.891, 95% CI: 1.188-3.010, P = 0.007) and rs1801133 (adjusted HR = 1.499, 95% CI: 1.141-1.971, P = 0.004) were independently associated with an increased risk of major cardiovascular events, and exhibited cumulative effect on even-free survival (adjusted HR = 1.810, 95% CI: 1.179-2.802, P = 0.007). In conclusion, rs11206510 and rs1801133 were independent risk factors for clinical outcome in CAD patients treated with statins.
Keywords: Statin; coronary artery disease; major cardiovascular event; prognosis.
IJCEP Copyright © 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LDL-c-linked SNPs are associated with LDL-c and myocardial infarction despite lipid-lowering therapy in patients with established vascular disease.Eur J Clin Invest. 2014 Feb;44(2):184-91. doi: 10.1111/eci.12206. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Eur J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24251769
-
Prospective association of a genetic risk score with major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(51):e9473. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009473. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29390587 Free PMC article.
-
Common variants of HMGCR, CETP, APOAI, ABCB1, CYP3A4, and CYP7A1 genes as predictors of lipid-lowering response to atorvastatin therapy.DNA Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;29(10):629-37. doi: 10.1089/dna.2009.1008. DNA Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20578904
-
2017 Taiwan lipid guidelines for high risk patients.J Formos Med Assoc. 2017 Apr;116(4):217-248. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2016.11.013. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Formos Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28242176 Review.
-
Rationale and design of the LURIC study--a resource for functional genomics, pharmacogenomics and long-term prognosis of cardiovascular disease.Pharmacogenomics. 2001 Feb;2(1 Suppl 1):S1-73. doi: 10.1517/14622416.2.1.S1. Pharmacogenomics. 2001. PMID: 11258203 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of the CYP7A1 Gene Polymorphisms Located in the Promoter and Enhancer Regions with the Risk of Acute Coronary Syndrome, Plasma Cholesterol, and the Incidence of Diabetes.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 9;12(3):617. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030617. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540230 Free PMC article.
-
Homocysteine concentration in coronary artery disease and severity of coronary lesions.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18474. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18474. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38896027 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) gene polymorphisms are associated with increased LDL-cholesterol levels and the incidence of subclinical atherosclerosis.Biomol Biomed. 2025 Mar 7;25(4):822-832. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10764. Biomol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 39207177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Catapano AL, Farnier M, Foody JM, Toth PP, Tomassini JE, Brudi P, Tershakovec AM. Combination therapy in dyslipidemia: where are we now? Atherosclerosis. 2014;237:319–335. - PubMed
-
- van der Valk FM, Bernelot Moens SJ, Verweij SL, Strang AC, Nederveen AJ, Verberne HJ, Nurmohamed MT, Baeten DL, Stroes ES. Increased arterial wall inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis is reduced by statin therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75:1848–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous