Effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on systemic inflammation and metabolic markers in patients undergoing haemodialysis and/or peritoneal dialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31969148
- PMCID: PMC6977292
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-020-1004-1
Effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on systemic inflammation and metabolic markers in patients undergoing haemodialysis and/or peritoneal dialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: This systematic review aimed to investigate whether non-surgical periodontal therapy (NSPT) can reduce systemic inflammatory levels and improve metabolism in patients undergoing haemodialysis (HD) and/or peritoneal dialysis (PD).
Methods: Electronic databases (PubMed, EMBASE, CENTRAL, CNKI, and WFPD) were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) performed through July 2019. The risk of bias within studies was assessed with the Cochrane Collaboration's risk assessment tool. The systemic inflammatory and metabolic outcomes included the highly sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumour necrosis factor-a (TNF-a), the albumin (Alb), and lipid metabolite levels. Meta-analyses (MAs) were performed to calculate the overall effect size where appropriate.
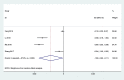
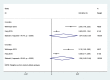
Results: Five RCTs were included in this study. Compared with untreated periodontitis groups, the dialysis patients after NSPT significantly showed decreased hs-CRP levels at less than or equal to 2 months (standardized mean difference: - 1.53, 95% confidence interval - 2.95 to - 0.11). No significant difference was found in IL-6 and Alb levels following NSPT at either the 3- or 6- month follow-ups. No MAs could be performed on the TNF-a level and the lipid metabolic markers.
Conclusions: NSPT can moderately reduce serum hs-CRP levels in HD and/or PD patients, but did not significantly change IL-6 or Alb levels. For TNF-a and lipid metabolism markers, no sufficient evidence supports that these levels are changed after NSPT. Additional scientific research is necessary to assess the effects of NSPT on systemic inflammation and metabolic parameters in dialysis patients.
Keywords: End-stage renal disease; Haemodialysis; Non-surgical periodontal treatment; Peritoneal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of non-surgical periodontal treatment on cytokines/adipocytokines levels among periodontitis patients with or without obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Oct 5;23(1):717. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03383-3. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37798684 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of periodontal treatment on inflammation and oxidative stress markers in patients with metabolic syndrome.J Periodontal Res. 2016 Aug;51(4):489-98. doi: 10.1111/jre.12328. Epub 2015 Nov 7. J Periodontal Res. 2016. PMID: 26547140
-
Inflammation and oxidative stress in end-stage renal disease patients treated with hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.Int J Artif Organs. 2009 Dec;32(12):872-82. doi: 10.1177/039139880903201206. Int J Artif Organs. 2009. PMID: 20037892
-
The effects of peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis on serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, interleukin-10 and C-reactive-protein levels.Mediators Inflamm. 2004 Jun;13(3):201-4. doi: 10.1080/09511920410001713493. Mediators Inflamm. 2004. PMID: 15223612 Free PMC article.
-
Serum C-Reactive Protein and Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 28;12:706432. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.706432. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34394107 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Implication of serum and salivary albumin tests in the recent oral health related epidemiological studies: A narrative review.Saudi Dent J. 2024 May;36(5):698-707. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2024.02.019. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Saudi Dent J. 2024. PMID: 38766281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fistula first, catheter last: can the mouth be second?Front Nephrol. 2024 May 23;4:1385544. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2024.1385544. eCollection 2024. Front Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38846514 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Association between Dental Scaling and Reduced Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 24;18(17):8910. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18178910. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34501499 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Response in Oral Biofilm during Pregnancy: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 19;14(22):4894. doi: 10.3390/nu14224894. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432584 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical response to nonsurgical periodontal therapy is associated with decreased serum leukocyte count and uric acid levels in kidney transplant recipients.J Appl Oral Sci. 2024 Sep 30;32:e20240206. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2024-0206. eCollection 2024. J Appl Oral Sci. 2024. PMID: 39356952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astor BC, Matsushita K, Gansevoort RT, van der Velde M, Woodward M, Levey AS, et al. Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with mortality and end-stage renal disease. A collaborative meta-analysis of kidney disease population cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011;79:1331–1340. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.550. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

