PI4KIIIβ is a therapeutic target in chromosome 1q-amplified lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31969487
- PMCID: PMC7702266
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax3772
PI4KIIIβ is a therapeutic target in chromosome 1q-amplified lung adenocarcinoma
Erratum in
-
Erratum for the Research Article: "PI4KIIIβ is a therapeutic target in chromosome 1q-amplified lung adenocarcinoma" by X. Tan, P. Banerjee, E. A. Pham, F. U. N. Rutaganira, K. Basu, N. Bota-Rabassedas, H.-F. Guo, C. L. Grzeskowiak, X. Liu, J. Yu, L. Shi, D. H. Peng, B. L. Rodriguez, J. Zhang, V. Zheng, D. Y. Duose, L. M. Solis, B. Mino, M. G. Raso, C. Behrens, I. I. Wistuba, K. L. Scott, M. Smith, K. Nguyen, G. Lam, I. Choong, A. Mazumdar, J. L. Hill, D. L. Gibbons, P. H. Brown, W. K. Russell, K. Shokat, C. J. Creighton, J. S. Glenn, J. M. Kurie.Sci Transl Med. 2020 Mar 18;12(535):eabb5995. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abb5995. Sci Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32188723 No abstract available.
Abstract
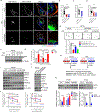
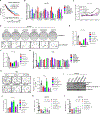
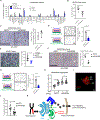
Heightened secretion of protumorigenic effector proteins is a feature of malignant cells. Yet, the molecular underpinnings and therapeutic implications of this feature remain unclear. Here, we identify a chromosome 1q region that is frequently amplified in diverse cancer types and encodes multiple regulators of secretory vesicle biogenesis and trafficking, including the Golgi-dedicated enzyme phosphatidylinositol (PI)-4-kinase IIIβ (PI4KIIIβ). Molecular, biochemical, and cell biological studies show that PI4KIIIβ-derived PI-4-phosphate (PI4P) synthesis enhances secretion and accelerates lung adenocarcinoma progression by activating Golgi phosphoprotein 3 (GOLPH3)-dependent vesicular release from the Golgi. PI4KIIIβ-dependent secreted factors maintain 1q-amplified cancer cell survival and influence prometastatic processes in the tumor microenvironment. Disruption of this functional circuitry in 1q-amplified cancer cells with selective PI4KIIIβ antagonists induces apoptosis and suppresses tumor growth and metastasis. These results support a model in which chromosome 1q amplifications create a dependency on PI4KIIIβ-dependent secretion for cancer cell survival and tumor progression.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
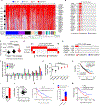
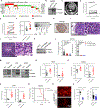
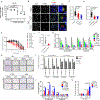
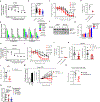

References
-
- Paltridge JL, Belle L, Khew-Goodall Y, The secretome in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1834, 2233–2241 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Coussens LM, Fingleton B, Matrisian LM, Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and tribulations. Science 295, 2387–2392 (2002). - PubMed
-
- McMillin DW, Negri JM, Mitsiades CS, The role of tumour-stromal interactions in modifying drug response: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12, 217–228 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

