Mechanism of adrenergic CaV1.2 stimulation revealed by proximity proteomics
- PMID: 31969708
- PMCID: PMC7018383
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-1947-z
Mechanism of adrenergic CaV1.2 stimulation revealed by proximity proteomics
Abstract
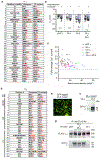
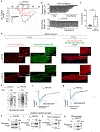
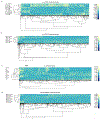
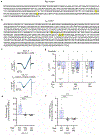
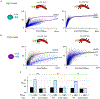
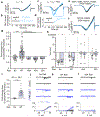
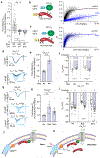
Increased cardiac contractility during the fight-or-flight response is caused by β-adrenergic augmentation of CaV1.2 voltage-gated calcium channels1-4. However, this augmentation persists in transgenic murine hearts expressing mutant CaV1.2 α1C and β subunits that can no longer be phosphorylated by protein kinase A-an essential downstream mediator of β-adrenergic signalling-suggesting that non-channel factors are also required. Here we identify the mechanism by which β-adrenergic agonists stimulate voltage-gated calcium channels. We express α1C or β2B subunits conjugated to ascorbate peroxidase5 in mouse hearts, and use multiplexed quantitative proteomics6,7 to track hundreds of proteins in the proximity of CaV1.2. We observe that the calcium-channel inhibitor Rad8,9, a monomeric G protein, is enriched in the CaV1.2 microenvironment but is depleted during β-adrenergic stimulation. Phosphorylation by protein kinase A of specific serine residues on Rad decreases its affinity for β subunits and relieves constitutive inhibition of CaV1.2, observed as an increase in channel open probability. Expression of Rad or its homologue Rem in HEK293T cells also imparts stimulation of CaV1.3 and CaV2.2 by protein kinase A, revealing an evolutionarily conserved mechanism that confers adrenergic modulation upon voltage-gated calcium channels.
Figures





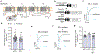

Comment in
-
Suspect that modulates the heartbeat is ensnared.Nature. 2020 Jan;577(7792):624-626. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-00096-3. Nature. 2020. PMID: 31988403 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cachelin AB, de Peyer JE, Kokubun S & Reuter H Ca2+ channel modulation by 8-bromocyclic AMP in cultured heart cells. Nature 304, 462–464 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Tsien RW, Giles W & Greengard P Cyclic AMP mediates the effects of adrenaline on cardiac purkinje fibres. Nat New Biol 240, 181–183 (1972). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 HL120826/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113136/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126735/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146149/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007343/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121253/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007854/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL160520/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL140934/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL142178/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

