Systemic Evaluation on the Pharmacokinetics of Platinum-Based Anticancer Drugs From Animal to Cell Level: Based on Total Platinum and Intact Drugs
- PMID: 31969818
- PMCID: PMC6960190
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01485
Systemic Evaluation on the Pharmacokinetics of Platinum-Based Anticancer Drugs From Animal to Cell Level: Based on Total Platinum and Intact Drugs
Abstract
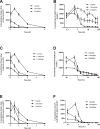
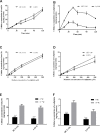
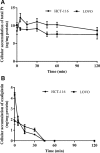
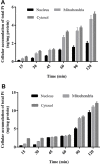
Cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin are the common platinum-based anticancer drugs widely used in the chemotherapeutic treatment of solid tumors in clinic. However, the comprehensive pharmacokinetics of platinum-based anticancer drugs has not been fully understood yet. This leads to many limitations for the further studies on their pharmacology and toxicology. In this study, we conduct a systemic evaluation on the pharmacokinetics of three platinum analogues at animal and cell levels, with quantification of both total platinum and intact drugs. A detailed animal study to address and compare the different pharmacokinetic behaviors of three platinum analogues has been conducted in three biological matrices: blood, plasma, and ultrafiltrate plasma. Carboplatin showed an obviously different pharmacokinetic characteristic from cisplatin and oxaliplatin. On the one hand, carboplatin has the highest proportion of Pt distribution in ultrafiltrate plasma. On the other hand, carboplatin has the highest intact drug exposure and longest intact drug elimination time in blood, plasma, and ultrafiltrate plasma, which may explain its high hematotoxicity. Additionally, the cellular and subcellular pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin in two colon cancer HCT-116/LOVO cell lines has been elucidated for the first time. The biotransformation of intact oxaliplatin in cells was rapid with a fast elimination, however, the generated platinum-containing metabolites still exist within cells. The distribution of total platinum in the cytosol is higher than in the mitochondria, followed by the nucleus. Enrichment of platinum in mitochondria may affect the respiratory chain or energy metabolism, and further lead to cell apoptosis, which may indicate mitochondria as another potential target for efficacy and toxicity of oxaliplatin.
Keywords: carboplatin; cisplatin; oxaliplatin; pharmacokinetics; total platinum.
Copyright © 2020 Qin, Ren, Yuan, Chen, Lu, Li, Zhang, Chen and Zhao.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of intravenous oxaliplatin, cisplatin, and carboplatin in nonhuman primates.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Feb 15;11(4):1669-74. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1807. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15746072
-
Sensitive inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry assay for the determination of platinum originating from cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin in human plasma ultrafiltrate.J Mass Spectrom. 2006 Sep;41(9):1186-94. doi: 10.1002/jms.1087. J Mass Spectrom. 2006. PMID: 16929560
-
Oxaliplatin: pharmacokinetics and chronopharmacological aspects.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000 Jan;38(1):1-21. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200038010-00001. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000. PMID: 10668856 Review.
-
Comparative pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin (L-OHP) and carboplatin (CBDCA) in mice with reference to circadian dosing time.Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1994 Dec;15(9):761-73. doi: 10.1002/bdd.2510150904. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1994. PMID: 7888604
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin: a critical review.Clin Cancer Res. 2000 Apr;6(4):1205-18. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10778943 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Sodium Thiosulfate as an Otoprotectant in Patients With Cancer Treated With Platinum Compounds: A Review of the Literature.J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 20;42(18):2219-2232. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.02353. Epub 2024 Apr 22. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38648563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-based knockout screening identifies the loss of MIEF2 to enhance oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;12:881487. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.881487. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36106106 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Oxaliplatin Long-Circulating Liposomes.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 20;2021:5949804. doi: 10.1155/2021/5949804. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33987441 Free PMC article.
-
Platinum Accumulation and Cancer-Related Fatigue, Correlation With IL-8, TNF-α and Hemocytes.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 7;12:658792. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.658792. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34557089 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophosphamide-induced multiple organ dysfunctions: unravelling of dose dependent toxic impact on biochemistry and histology.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Dec 17;13(6):tfae201. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae201. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39698395
References
-
- Bandu R., Ahn H. S., Lee J. W., Kim Y. W., Choi S. H., Kim H. J., et al. (2015). Liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric (LC/ESI-MS/MS) study for the identification and characterization of in vivo metabolites of cisplatin in rat kidney cancer tissues: online hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) exchange study. PloS One 10, e0134027. 10.1371/journal.pone.0134027 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corte-Rodriguez M., Espina M., Sierra L. M., Blanco E., Ames T., Montes-Bayon M., et al. (2015). Quantitative evaluation of cellular uptake, DNA incorporation and adduct formation in cisplatin sensitive and resistant cell lines: Comparison of different Pt-containing drugs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 98, 69–77. 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.08.112 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

