Functional Characterization of Invertase Inhibitors PtC/VIF1 and 2 Revealed Their Involvements in the Defense Response to Fungal Pathogen in Populus trichocarpa
- PMID: 31969894
- PMCID: PMC6960229
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01654
Functional Characterization of Invertase Inhibitors PtC/VIF1 and 2 Revealed Their Involvements in the Defense Response to Fungal Pathogen in Populus trichocarpa
Abstract
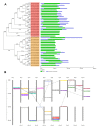
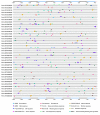
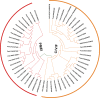
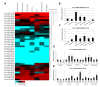
In higher plants, cell wall invertase (CWI) and vacuolar invertase (VI) were considered to be essential coordinators in carbohydrate partitioning, sink strength determination, and stress responses. An increasing body of evidence revealed that the tight regulation of CWI and VI substantially depends on the post-translational mechanisms, which were mediated by small proteinaceous inhibitors (C/VIFs, Inhibitor of β-Fructosidases). As yet, the extensive survey of the molecular basis and biochemical property of C/VIFs remains largely unknown in black cottonwood (Populus trichocarpa Torr. & A. Gray), a model species of woody plants. In the present work, we have initiated a systematic review of the genomic structures, phylogenies, cis-regulatory elements, and conserved motifs as well as the tissue-specific expression, resulting in the identification of 39 genes encoding C/VIF in poplar genome. We characterized two putative invertase inhibitors PtC/VIF1 and 2, showing predominant transcript levels in the roots and highly divergent responses to the selected stress cues including fusarium wilt, drought, ABA, wound, and senescence. In silico prediction of the signal peptide hinted us that they both likely had the apoplastic targets. Based on the experimental visualization via the transient and stable transformation assays, we confirmed that PtC/VIF1 and 2 indeed secreted to the extracellular compartments. Further validation of their recombinant enzymes revealed that they displayed the potent inhibitory affinities on the extracted CWI, supporting the patterns that act as the typical apoplastic invertase inhibitors. To our knowledge, it is the first report on molecular characterization of the functional C/VIF proteins in poplar. Our results indicate that PtC/VIF1 and 2 may exert essential roles in defense- and stress-related responses. Moreover, novel findings of the up- and downregulated C/VIF genes and functional enzyme activities enable us to further unravel the molecular mechanisms in the promotion of woody plant performance and adapted-biotic stress, underlying the homeostatic control of sugar in the apoplast.
Keywords: apoplast; defense response; drought; invertase inhibitor; pathogen; poplar; sucrose.
Copyright © 2020 Su, Han, Min, Zhou, Zhang, Zhao and Fang.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Survey of Invertase Encoding Genes and Functional Characterization of an Extracellular Fungal Pathogen-Responsive Invertase in Glycine max.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 14;19(8):2395. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082395. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30110937 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Profiling of Populus Roots Challenged with Fusarium Reveals Differential Responsive Patterns of Invertase and Invertase Inhibitor-Like Families within Carbohydrate Metabolism.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Jan 27;7(2):89. doi: 10.3390/jof7020089. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33513923 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of a cell wall invertase inhibitor StInvInh1 revealed its involvement in potato microtuber size in vitro.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 3;13:1015815. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1015815. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36262645 Free PMC article.
-
Sucrose and invertases, a part of the plant defense response to the biotic stresses.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Jun 23;5:293. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00293. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25002866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic regulation of leaf senescence: interactions of sugar signalling with biotic and abiotic stress responses.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008 Sep;10 Suppl 1:50-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2008.00086.x. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2008. PMID: 18721311 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insight into Aspartate Metabolic Pathways in Populus: Linking the Root Responsive Isoenzymes with Amino Acid Biosynthesis during Incompatible Interactions of Fusarium solani.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 7;23(12):6368. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126368. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742809 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Survey and Expression Analyses of Hexokinase Family in Poplar (Populus trichocarpa).Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 3;11(15):2025. doi: 10.3390/plants11152025. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35956502 Free PMC article.
-
A Fructan Exohydrolase from Maize Degrades Both Inulin and Levan and Co-Exists with 1-Kestotriose in Maize.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 13;22(10):5149. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105149. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34068004 Free PMC article.
-
A Vacuolar Invertase CsVI2 Regulates Sucrose Metabolism and Increases Drought Tolerance in Cucumis sativus L.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 24;23(1):176. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010176. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008600 Free PMC article.
-
Editing Metabolism, Sex, and Microbiome: How Can We Help Poplar Resist Pathogens?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1308. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021308. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

