Sarcopenia in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
- PMID: 31970027
- PMCID: PMC6971421
Sarcopenia in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the prevalence of pre-sarcopenia and sarcopenia and their relationship with clinical variables, physical activity, quality of life, and diet in patients with heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Methods: We performed a cross-sectional study in patients with HFrEF and matched controls. Clinical, laboratory analysis, dual-emission X-ray densitometry, handgrip strength, and physical activity level questionnaire assessments were performed. Echocardiography, quality of life, gait speed, and 24-hour nutritional recall questionnaire were also analyzed. Pre-sarcopenia and sarcopenia were defined according to the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People with the cut-off points of the Foundation for the National Institute of Health.
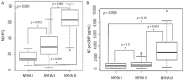
Results: 79 patients and 143 controls were enrolled. Pre-sarcopenia was found in 30.4%, and sarcopenia in 10.1% of the patients. Pre-sarcopenic patients were older and shorter, and had more fractures, higher calcemia, and creatinine (P < 0.05). Sarcopenic patients were older and had higher creatinine and TSH (P < 0.05). After multiple logistic regression analysis, only age was associated with pre-sarcopenia (OR: 1.046; CI 1.004-1.095; P = 0.04) and SP (OR: 1.119; CI 1.039-1.229; P = 0.008). Women with HFrEF presented higher lean mass than controls (P < 0.001), but were weaker (P < 0.001), while men presented lower lean mass (P < 0.001). Low gait speed was associated with right ventricular dysfunction (P = 0.016) and lower left ventricular ejection fraction (P = 0.037).
Conclusion: Pre-sarcopenia and sarcopenia were associated with aging. Despite having higher lean mass, women with HFrEF were weaker. Low gait speed was associated with biventricular systolic dysfunction.
Keywords: Frailty; heart failure; muscle wasting; sarcopenia; skeletal myopathy.
AJCD Copyright © 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Wilson D, Jackson T, Sapey E, Lord JM. Frailty and sarcopenia: the potential role of an aged immune system. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;36:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Morley JE, Vellas B, van Kan GA, Anker SD, Bauer JM, Bernabei R, Cesari M, Chumlea WC, Doehner W, Evans J, Fried LP, Guralnik JM, Katz PR, Malmstrom TK, McCarter RJ, Gutierrez Robledo LM, Rockwood K, von Haehling S, Vandewoude MF, Walston J. Frailty consensus: a call to action. J Am Med Dir Assocation. 2013;14:392–7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y, Schneider SM, Topinková E, Vandewoude M, Zamboni M European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: report of the European working group on sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing. 2010;39:412–23. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
