Value of dynamic plasma cell-free DNA monitoring in septic shock syndrome: A case report
- PMID: 31970188
- PMCID: PMC6962064
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i1.200
Value of dynamic plasma cell-free DNA monitoring in septic shock syndrome: A case report
Abstract
Background: Mortality due to septic shock is relatively high. The dynamic monitoring of plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) can guide the treatment of septic shock.
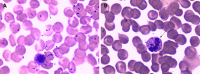
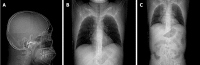
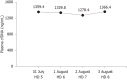
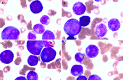
Case summary: Herein, we present a typical case of septic shock syndrome caused by the bacilli Acinetobacter baumannii and Pantoea. The patient complained of abdominal pain, fever and chills upon admission to the Emergency Department. Marked decreases in white blood cells and procalcitonin (PCT) were observed after the patient received continuous renal replacement and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Plasma cfDNA levels were consistently high, peaking at 1366.40 ng/mL, as measured by a duplex real-time PCR assay with an internal control, which was developed as a novel method for the accurate quantification of cfDNA. The patient died of septic shock on HD 8, suggesting that cfDNA could be used to monitor disease progression more effectively than PCT and the other inflammatory factors measured in this case.
Conclusion: CfDNA may be a promising marker that complements other inflammatory factors to monitor disease progression in patients with septic shock.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Case report; Cell-free DNA; Septic shock.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell Free DNA and Procalcitonin as Early Markers of Complications in ICU Patients with Multiple Trauma and Major Surgery.Clin Lab. 2016 Dec 1;62(12):2395-2404. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2016.160615. Clin Lab. 2016. PMID: 28164563
-
[Role of procalcitonin in monitoring the antibiotic therapy in septic surgical patients].Chirurgia (Bucur). 2012 Jan-Feb;107(1):71-8. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2012. PMID: 22480120 Romanian.
-
Procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker for sepsis/septic shock in the emergency department; a study based on Sepsis-3 definition.Am J Emerg Med. 2019 Feb;37(2):272-276. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2018.05.047. Epub 2018 May 26. Am J Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 29861371
-
Procalcitonin under Investigation as a Means of Detecting Severe Sepsis, Septic Shock and Bacteremia at Emergency Department, Rajavithi Hospital.J Med Assoc Thai. 2016 Feb;99 Suppl 2:S63-8. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016. PMID: 27266218
-
Usefulness of procalcitonin for diagnosis of infection in cardiac surgical patients.Crit Care Med. 2000 Sep;28(9):3171-6. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200009000-00008. Crit Care Med. 2000. PMID: 11008977
Cited by
-
Role of cell-free DNA levels in the diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis and bacteremia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 29;19(8):e0305895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305895. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39208340 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics of Severe COVID-19 Patients During Omicron Epidemic and a Nomogram Model Integrating Cell-Free DNA for Predicting Mortality: A Retrospective Analysis.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Oct 18;16:6735-6745. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S430101. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37873032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Annane D, Bellissant E, Cavaillon JM. Septic shock. Lancet. 2005;365:63–78. - PubMed
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:840–851. - PubMed
-
- House AA, Ronco C. Extracorporeal blood purification in sepsis and sepsis-related acute kidney injury. Blood Purif. 2008;26:30–35. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

