Hyperphosphorylated Tau, Increased Adenylate Cyclase 5 (ADCY5) Immunoreactivity, but No Neuronal Loss in ADCY5-Dyskinesia
- PMID: 31970214
- PMCID: PMC6962666
- DOI: 10.1002/mdc3.12873
Hyperphosphorylated Tau, Increased Adenylate Cyclase 5 (ADCY5) Immunoreactivity, but No Neuronal Loss in ADCY5-Dyskinesia
Abstract
Background: Adenylate cyclase 5 (ADCY5)-related dyskinesia is a childhood-onset movement disorder. Manifestations vary in frequency and severity and may include chorea, tremor, dystonia, facial twitches, myoclonus, axial hypotonia, and limb hypertonia. Psychosis is likely part of the broader spectrum. ADCY5 is widely expressed in the brain, especially in the striatum. Previous reports of brain autopsies of 2 subjects with likely ADCY5-dyskinesia were limited by the absence of a molecular diagnosis. In 1 case, normal gross pathology was reported. In the other case, ADCY5 expression was not examined and neuropathological findings were confounded by age and comorbidities.
Objectives: To examine ADCY5 expression and neuropathological changes in ADCY5-dyskinesia.
Methods: An extensive brain autopsy, including immunohistochemical analyses with antibodies to paired helical filament tau, α-synuclein, amyloid-β, microtubule-associated protein 2, and ADCY5, was performed.
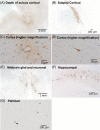
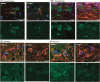
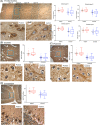
Results: The patient, with a p.M1029K ADCY5 variant, had severe dyskinesias from early childhood, later recurrent episodes of psychosis, and died at age 46. Gross pathology was unremarkable, but we detected increased immunoreactivity for ADCY5 in neurons in multiple brain regions. Despite no history of brain trauma to suggest chronic traumatic encephalopathy, we found tau deposits in the deep cortical sulci, midbrain, and hippocampus with minimal amyloid pathology and no Lewy bodies.
Conclusions: We present the first brain autopsy findings in a molecularly proven case of ADCY5-dyskinesia, showing increased ADCY5 immunoreactivity in neurons and evidence of tau deposition. Additional patients will need to be studied to determine whether increased immunoreactivity for ADCY5 is a signature for ADCY5-dyskinesia and whether this disease has a tauopathy component.
Keywords: ADCY5‐dyskinesia; neurogenetics; neuropathology; tau.
© 2019 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by grants R01NS069719 and P50AG005136 from the National Institutes of Health, Merit Review Award Number 101 CX001702 from the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, and the Nancy and Buster Alvord Endowment. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Vijiaratnam N, Newby R, Kempster PA. Depression and psychosis in ADCY5‐related dyskinesia‐part of the phenotypic spectrum? J Clin Neurosci 2018;57:167–168. - PubMed
-
- Bohlega SA, Abou‐Al‐Shaar H, AlDakheel A, et al. Autosomal recessive ADCY5‐related dystonia and myoclonus: expanding the genetic spectrum of ADCY5‐related movement disorders. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2019;64:145–149. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

