Exercise in neuromuscular disorders: a promising intervention
- PMID: 31970319
- PMCID: PMC6955632
Exercise in neuromuscular disorders: a promising intervention
Abstract
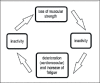
Although performing exercise studies in patients with neuromuscular disorders (NMD) is difficult, the number of randomized controlled trials is steadily increasing. There is growing evidence for a positive effect of aerobic exercise in several NMD, on the other hand, the evidence for the effect of strength training is still scarce. Many NMD patients are captured in a vicious circle of physical inactivity, and it is important to let patients adhere to an active lifestyle, in order to prevent further chronic cardiovascular and muscle deconditioning and increased cardiovascular health risks. Exercise has to be prescribed as if it is medicine, in order to increase the adherence of patients and to optimize the efficacy of the intervention. Exercise in NMD is safe, although for some metabolic myopathies there is a contraindication for strenuous exercise. In NMD known to affect cardiac muscle, it is usually safe to exercise, but the consultation of a cardiologist is advised. Based on recent research, an increase in physical activity of moderate intensity and of sufficient duration, i.e. a physically active lifestyle, could be at least as effective and relevant as physical training. Underlying mechanisms of effect of exercise could be the influence of epigenetic mechanisms and the anti-inflammatory effect of exercise, but further studies are needed to confirm these hypotheses.
Keywords: exercise; neuromuscular disorders; physical activity.
©2019 Gaetano Conte Academy - Mediterranean Society of Myology, Naples, Italy.
Figures
References
-
- Fowler WMJ. Role of physical activity and exercise training in neuromuscular diseases. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2002;81(Suppl 11):S187-95. - PubMed
-
- Aitkens SG, McCrory MA, Kilmer DD, et al. Moderate resistance exercise program: its effect in slowly progressive neuromuscular disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1993;74:711-5. - PubMed
-
- Kilmer DD, McCrory MA, Wright NC, et al. The effect of a high resistance exercise program in slowly progressive neuromuscular disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1994;75:560-3. - PubMed
-
- Tollback A, Eriksson S, Wredenberg A, et al. Effects of high resistance training in patients with myotonic dystrophy. Scand J Rehabil Med 1999;31:9-16. - PubMed
-
- Voet NB, van der Kooi EL, Riphagen II, et al. Strength training and aerobic exercise training for muscle disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;7:CD003907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical