Pustular Psoriasis: The Dawn of a New Era
- PMID: 31971600
- PMCID: PMC9128889
- DOI: 10.2340/00015555-3388
Pustular Psoriasis: The Dawn of a New Era
Abstract
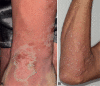
Pustular psoriasis is a clinically heterogeneous entity of different, orphan disease subtypes, among which the most clearly defined are generalized pustular psoriasis, palmoplantar psoriasis, and acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau. Although phenotypically and genetically distinct from psoriasis vulgaris, these subtypes may be associated with plaque psoriasis lesions, establishing the rationale for their inclusion in the psoriasis spectrum. Unlike psoriasis, however, their genetic background is thought to be mainly monogenic, as shown by the recent identification of mutations in 3 different genes of the skin innate immune system; IL36RN, CARD14 and AP1S3. These major advances in the understanding of the disease pathogenesis have led to the design and ongoing development of tailored therapeutic approaches, which are highly necessary given the refractory nature of pustular psoriasis in response to most available antipsoriatic drugs.
Keywords: generalized pustular psoriasis; interleukin-36; palmoplantar pustulosis; pustular psoriasis; pustulosis.
Figures

References
-
- Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 496–509. - PubMed
-
- Naldi L, Gambini D. The clinical spectrum of psoriasis. Clin Dermatol 2007; 25: 510–518. - PubMed
-
- Augey F, Renaudier P, Nicolas JF. Generalized pustular psoriasis (Zumbusch): a French epidemiological survey. Eur J Dermatol 2006; 16: 669–673. - PubMed
-
- Ohkawara A, Yasuda H, Kobayashi H, Inaba Y, Ogawa H, Hashimoto I, et al. . Generalized pustular psoriasis in Japan: two distinct groups formed by differences in symptoms and genetic background. Acta Derm Venereol 1996: 76: 68–71. - PubMed
-
- Baker H, Ryan TJ. Generalized pustular psoriasis. A clinical and epidemiological study of 104 cases. Br J Dermatol 1968; 80: 771–793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

