Structural mechanisms of transient receptor potential ion channels
- PMID: 31972006
- PMCID: PMC7054860
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201811998
Structural mechanisms of transient receptor potential ion channels
Abstract
Transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channels are evolutionarily ancient sensory proteins that detect and integrate a wide range of physical and chemical stimuli. TRP channels are fundamental for numerous biological processes and are therefore associated with a multitude of inherited and acquired human disorders. In contrast to many other major ion channel families, high-resolution structures of TRP channels were not available before 2013. Remarkably, however, the subsequent "resolution revolution" in cryo-EM has led to an explosion of TRP structures in the last few years. These structures have confirmed that TRP channels assemble as tetramers and resemble voltage-gated ion channels in their overall architecture. But beyond the relatively conserved transmembrane core embedded within the lipid bilayer, each TRP subtype appears to be endowed with a unique set of soluble domains that may confer diverse regulatory mechanisms. Importantly, TRP channel TR structures have revealed sites and mechanisms of action of numerous synthetic and natural compounds, as well as those for endogenous ligands such as lipids, Ca2+, and calmodulin. Here, I discuss these recent findings with a particular focus on the conserved transmembrane region and how these structures may help to rationally target this important class of ion channels for the treatment of numerous human conditions.
© 2020 Cao.
Figures
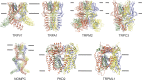
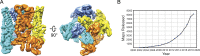

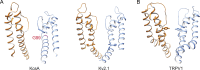


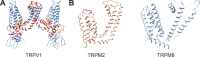
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

