Communication, Cross Talk, and Signal Integration in the Adult Hippocampal Neurogenic Niche
- PMID: 31972145
- PMCID: PMC7184932
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.029
Communication, Cross Talk, and Signal Integration in the Adult Hippocampal Neurogenic Niche
Abstract
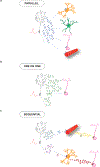
Radial glia-like neural stem cells (RGLs) in the dentate gyrus subregion of the hippocampus give rise to dentate granule cells (DGCs) and astrocytes throughout life, a process referred to as adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sensitive to experiences, suggesting that it may represent an adaptive mechanism by which hippocampal circuitry is modified in response to environmental demands. Experiential information is conveyed to RGLs, progenitors, and adult-born DGCs via the neurogenic niche that is composed of diverse cell types, extracellular matrix, and afferents. Understanding how the niche performs its functions may guide strategies to maintain its health span and provide a permissive milieu for neurogenesis. Here, we first discuss representative contributions of niche cell types to regulation of neural stem cell (NSC) homeostasis and maturation of adult-born DGCs. We then consider mechanisms by which the activity of multiple niche cell types may be coordinated to communicate signals to NSCs. Finally, we speculate how NSCs integrate niche-derived signals to govern their regulation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests
The authors declare no competing financial and non-financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activity-dependent signaling mechanisms regulating adult hippocampal neural stem cells and their progeny.Neurosci Bull. 2014 Aug;30(4):542-56. doi: 10.1007/s12264-014-1453-5. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Neurosci Bull. 2014. PMID: 25082534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt Signaling in the Adult Hippocampal Neurogenic Niche.Stem Cells. 2022 Jul 27;40(7):630-640. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxac027. Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35446432
-
Transcriptional regulation of neural stem cell expansion in the adult hippocampus.Elife. 2022 Jan 4;11:e72195. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72195. Elife. 2022. PMID: 34982030 Free PMC article.
-
A developmental perspective on adult hippocampal neurogenesis.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013 Nov;31(7):640-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23588197 Review.
-
Development of Adult-Generated Cell Connectivity with Excitatory and Inhibitory Cell Populations in the Hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 22;35(29):10600-12. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3238-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26203153 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Traumatic brain injury promotes neurogenesis at the cost of astrogliogenesis in the adult hippocampus of male mice.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 18;15(1):5222. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49299-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38890340 Free PMC article.
-
Adult Neural Stem Cell Regulation by Small Non-coding RNAs: Physiological Significance and Pathological Implications.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 4;15:781434. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.781434. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35058752 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial activation and adult neurogenesis after brain stroke.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Mar;16(3):456-459. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.291383. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 32985465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robust Transcriptional Profiling and Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes With Low Input RNA Sequencing of Adult Hippocampal Neural Stem and Progenitor Populations.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jan 31;15:810722. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.810722. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35173579 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol, inflammation, and blood-brain barrier function in health and disease across development.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2022;161:209-249. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2021.06.009. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34801170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adamsky A, Kol A, Kreisel T, Doron A, Ozeri-Engelhard N, Melcer T, Refaeli R, Horn H, Regev L, Groysman M, et al. (2018). Astrocytic Activation Generates De Novo Neuronal Potentiation and Memory Enhancement. Cell 174, 59–71 e14. - PubMed
-
- Alfonso J, Le Magueresse C, Zuccotti A, Khodosevich K, and Monyer H (2012). Diazepam binding inhibitor promotes progenitor proliferation in the postnatal SVZ by reducing GABA signaling. Cell Stem Cell 10, 76–87. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez DD, Giacomini D, Yang SM, Trinchero MF, Temprana SG, Buttner KA, Beltramone N, and Schinder AF (2016). A disynaptic feedback network activated by experience promotes the integration of new granule cells. Science 354, 459–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

