Low catechol-O-methyltransferase and stress potentiate functional pain and depressive behavior, especially in female mice
- PMID: 31972854
- PMCID: PMC7282074
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001734
Low catechol-O-methyltransferase and stress potentiate functional pain and depressive behavior, especially in female mice
Abstract
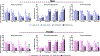
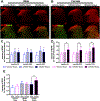
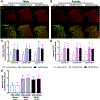
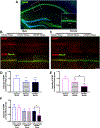
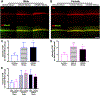
Low levels of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), an enzyme that metabolizes catecholamines, and stress, which potentiates catecholamine release from sympathetic nerves, are fundamental to chronic functional pain syndromes and comorbid depression, which predominantly affect females. Here, we sought to examine the independent and joint contributions of low COMT and stress to chronic functional pain and depression at the behavioral and molecular level. Male and female C57BL/6 mice received sustained systemic delivery of the COMT inhibitor OR486 over 14 days and underwent a swim stress paradigm on days 8 to 10. Pain and depressive-like behavior were measured over 14 days, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF; a factor involved in nociception and depression) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR; a stress-related receptor) expression were measured on day 14. We found that stress potentiates the effect of low COMT on functional pain and low COMT potentiates the effect of stress on depressive-like behavior. The joint effects of low COMT and stress on functional pain and depressive-like behavior were significantly greater in females vs males. Consistent with behavioral data, we found that stress potentiates COMT-dependent increases in spinal BDNF and low COMT potentiates stress-dependent decreases in hippocampal BDNF in females, but not males. Although low COMT increases spinal GR and stress increases hippocampal GR expression, these increases are not potentiated in the OR486 + stress group and are not sex-specific. These results suggest that genetic and environmental factors that enhance catecholamine bioavailability cause abnormalities in BDNF signaling and increase risk of comorbid functional pain and depression, especially among females.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
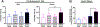
References
-
- Asher M, Asnaani A, Aderka IM. Gender differences in social anxiety disorder: A review. Clin Psychol Rev 2017;56:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa FR, Matsuda JB, Mazucato M, de Castro Franca S, Zingaretti SM, da Silva LM, Martinez-Rossi NM, Junior MF, Marins M, Fachin AL. Influence of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) gene polymorphisms in pain sensibility of Brazilian fibromialgia patients. Rheumatol Int 2012;32(2):427–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

