Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans LtxA Hijacks Endocytic Trafficking Pathways in Human Lymphocytes
- PMID: 31973183
- PMCID: PMC7168647
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9020074
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans LtxA Hijacks Endocytic Trafficking Pathways in Human Lymphocytes
Abstract
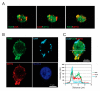
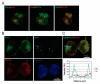
Leukotoxin (LtxA), from oral pathogen Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, is a secreted membrane-damaging protein. LtxA is internalized by β2 integrin LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18)-expressing leukocytes and ultimately causes cell death; however, toxin localization in the host cell is poorly understood and these studies fill this void. We investigated LtxA trafficking using multi-fluor confocal imaging, flow cytometry and Rab5a knockdown in human T lymphocyte Jurkat cells. Planar lipid bilayers were used to characterize LtxA pore-forming activity at different pHs. Our results demonstrate that the LtxA/LFA-1 complex gains access to the cytosol of Jurkat cells without evidence of plasma membrane damage, utilizing dynamin-dependent and presumably clathrin-independent mechanisms. Upon internalization, LtxA follows the LFA-1 endocytic trafficking pathways, as identified by co-localization experiments with endosomal and lysosomal markers (Rab5, Rab11A, Rab7, and Lamp1) and CD11a. Knockdown of Rab5a resulted in the loss of susceptibility of Jurkat cells to LtxA cytotoxicity, suggesting that late events of LtxA endocytic trafficking are required for toxicity. Toxin trafficking via the degradative endocytic pathway may culminate in the delivery of the protein to lysosomes or its accumulation in Rab11A-dependent recycling endosomes. The ability of LtxA to form pores at acidic pH may result in permeabilization of the endosomal and lysosomal membranes.
Keywords: Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans; LFA-1; RTX toxin; leukotoxin (LtxA), endocytosis; localized aggressive periodontitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin induces cytosol acidification in LFA-1 expressing immune cells.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2016 Feb;31(1):106-14. doi: 10.1111/omi.12136. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26361372 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA) Requires Death Receptor Fas, in Addition to LFA-1, To Trigger Cell Death in T Lymphocytes.Infect Immun. 2019 Jul 23;87(8):e00309-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00309-19. Print 2019 Aug. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31109948 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA; Leukothera®): Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Applications.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Aug 26;11(9):489. doi: 10.3390/toxins11090489. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31454891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane localization of the Repeats-in-Toxin (RTX) Leukotoxin (LtxA) produced by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 18;13(10):e0205871. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205871. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30335797 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin: From mechanism to targeted anti-toxin therapeutics.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2020 Jun;35(3):85-105. doi: 10.1111/omi.12284. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32061022 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virulence Factors of the Periodontal Pathogens: Tools to Evade the Host Immune Response and Promote Carcinogenesis.Microorganisms. 2023 Jan 1;11(1):115. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010115. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36677408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans cytolethal distending toxin modulates host phagocytic function.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 31;13:1220089. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1220089. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37719670 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis Share Intracellular Disorders as the Main Meeting Point.Cells. 2021 Sep 13;10(9):2411. doi: 10.3390/cells10092411. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial Comments to the Special Issue: "Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans-Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogen".Pathogens. 2020 Jun 4;9(6):441. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9060441. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32512822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Linhartova I., Bumba L., Masin J., Basler M., Osicka R., Kamanova J., Prochazkova K., Adkins I., Hejnova-Holubova J., Sadilkova L., et al. RTX proteins: a highly diverse family secreted by a common mechanism. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010;34:1076–1112. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00231.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soloaga A., Veiga M.P., Garcia-Segura L.M., Ostolaza H., Brasseur R., Goni F.M. Insertion of Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin in lipid bilayers as a non-transmembrane integral protein: prediction and experiment. Mol. Microbiol. 1999;31:1013–1024. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01225.x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

