Targeting the RNA Polymerase I Transcription for Cancer Therapy Comes of Age
- PMID: 31973211
- PMCID: PMC7072222
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9020266
Targeting the RNA Polymerase I Transcription for Cancer Therapy Comes of Age
Abstract
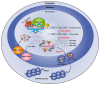
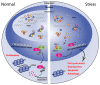
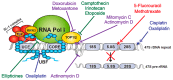
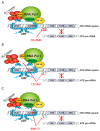
Transcription of the ribosomal RNA genes (rDNA) that encode the three largest ribosomal RNAs (rRNA), is mediated by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) and is a key regulatory step for ribosomal biogenesis. Although it has been reported over a century ago that the number and size of nucleoli, the site of ribosome biogenesis, are increased in cancer cells, the significance of this observation for cancer etiology was not understood. The realization that the increase in rRNA expression has an active role in cancer progression, not only through increased protein synthesis and thus proliferative capacity but also through control of cellular check points and chromatin structure, has opened up new therapeutic avenues for the treatment of cancer through direct targeting of Pol I transcription. In this review, we discuss the rational of targeting Pol I transcription for the treatment of cancer; review the current cancer therapeutics that target Pol I transcription and discuss the development of novel Pol I-specific inhibitors, their therapeutic potential, challenges and future prospects.
Keywords: CX-5461; RNA polymerase I transcription; cancer therapy; ribosome biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Ross Hannan is chair of the scientific advisory board of Pimera Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of RNA Polymerase I Transcription in Development, Disease, and Aging.Annu Rev Biochem. 2018 Jun 20;87:51-73. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-012612. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29589958 Review.
-
RNA Polymerases I and III in development and disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 28;136:49-63. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.03.027. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 35422389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is ribosome synthesis controlled by pol I transcription?Cell Cycle. 2007 Jan 1;6(1):11-5. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.1.3649. Epub 2007 Jan 9. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17245116 Review.
-
Beyond rRNA: nucleolar transcription generates a complex network of RNAs with multiple roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis.Genes Dev. 2022 Aug 1;36(15-16):876-886. doi: 10.1101/gad.349969.122. Genes Dev. 2022. PMID: 36207140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inositol pyrophosphates regulate RNA polymerase I-mediated rRNA transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem J. 2015 Feb 15;466(1):105-14. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140798. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25423617 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Deregulated Ribosomal Biogenesis in Cancer.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 30;13(11):1593. doi: 10.3390/biom13111593. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38002277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gallic Acid Derivatives Propyl Gallate and Epigallocatechin Gallate Reduce rRNA Transcription via Induction of KDM2A Activation.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 25;12(1):30. doi: 10.3390/biom12010030. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 35053178 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides Targeting the Interaction Between Erb1 and Ytm1 Ribosome Assembly Factors.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Sep 1;8:718941. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.718941. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34540895 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of TCOF1 Gene in Health and Disease: Beyond Treacher Collins Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 1;22(5):2482. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052482. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribosome-Directed Therapies in Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 26;10(9):2088. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092088. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

