Cluster-Randomized Trial of Thrombolysis Implementation Support in Metropolitan and Regional Australian Stroke Centers: Lessons for Individual and Systems Behavior Change
- PMID: 31973599
- PMCID: PMC7033885
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012732
Cluster-Randomized Trial of Thrombolysis Implementation Support in Metropolitan and Regional Australian Stroke Centers: Lessons for Individual and Systems Behavior Change
Abstract
Background Intravenous thrombolytic therapy (IVT) with tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke is underutilized in many parts of the world. Randomized trials to test the effectiveness of thrombolysis implementation strategies are limited. Methods and Results This study aimed to test the effectiveness of a multicomponent, multidisciplinary tissue plasminogen activator implementation package in increasing the proportion of thrombolyzed cases while maintaining accepted benchmarks for low rates of intracranial hemorrhage and high rates of functional outcomes at 3 months. A cluster randomized controlled trial of 20 hospitals in the early stages of thrombolysis implementation across 3 Australian states was undertaken. Monitoring of IVT rates during the baseline period allowed hospitals (the unit of randomization) to be grouped into 3 baseline IVT strata-very low rates (0% to ≤4.0%); low rates (>4.0% to ≤10.0%); and moderate rates (>10.0%). Hospitals were randomized to an implementation package (experimental group) or usual care (control group) using a 1:1 ratio. The 16-month intervention was based on behavioral theory and analysis of the steps, roles, and barriers to rapid assessment for thrombolysis eligibility and involved comprehensive strategies addressing individual and system-level change. The primary outcome was the difference in tissue plasminogen activator proportions between the 2 groups postintervention. The absolute difference in postintervention IVT rates between intervention and control hospitals adjusted for baseline IVT rate and stratum was not significant (primary outcome rate difference=1.1% (95% CI -1.5% to 3.7%; P=0.38). Rates of intracranial hemorrhage remained below international benchmarks. Conclusions The implementation package resulted in no significant change in tissue plasminogen activator implementation, suggesting that ongoing support is needed to sustain initial modifications in behavior. Clinical Trial Registration URL: www.anzctr.org.au Unique identifiers: ACTRN12613000939796 and U1111-1145-6762.
Keywords: health system change; implementation; ischemic stroke; quality improvement; thrombolysis.
Figures
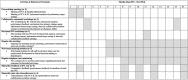
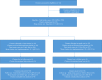
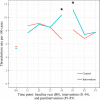
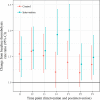
References
-
- Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, Parmar P, Krishnamurthi R, Chugh S, Mensah GA, Norrving B, Shiue I, Ng M, Estep K, Cercy K, Murray CJL, Forouzanfar MH; Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2013 and Stroke Experts Writing Group . Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:913–924. - PubMed
-
- Thrift AG, Thayabaranathan T, Howard G, Howard VJ, Rothwell PM, Feigin VL, Norrving B, Donnan GA, Cadilhac DA. Global stroke statistics. Int J Stroke. 2017;12:13–32. - PubMed
-
- Craig P, Dieppe P, Macintyre S, Michie S, Nazareth I, Petticrew M; Medical Research Council Guidance . Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new Medical Research Council guidance. [reprint in Int J Nurs Stud. 2013;50:587‐592; pmid: 23159157]. BMJ. 2008;337:a1655. - PubMed
-
- Quain DA, Parsons MW, Loudfoot AR, Spratt NJ, Evans MK, Russell ML, Royan AT, Moore AG, Miteff F, Hullick C. Improving access to acute stroke therapies: a controlled trial of organised pre‐hospital and emergency care. Med J Aust. 2008;189:429–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

