Recurrence of FSGS after Kidney Transplantation in Adults
- PMID: 31974287
- PMCID: PMC7015092
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.08970719
Recurrence of FSGS after Kidney Transplantation in Adults
Abstract
Background and objectives: FSGS recurrence after kidney transplantation is a major risk factor for graft loss. However, the natural history, clinical predictors, and response to treatment remain unclear because of small sample sizes and poor generalizability of single-center studies, and disease misclassification in registry-based studies. We therefore aimed to determine the incidence, predictors, and treatment response of recurrent FSGS in a large cohort of kidney transplant recipients.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: The Post-Transplant Glomerular Disease (TANGO) project is an observational, multicenter, international cohort study that aims to investigate glomerular disease recurrence post-transplantation. Transplant recipients were screened for the diagnosis of idiopathic FSGS between 2005 and 2015 and details were recorded about the transplant, clinical outcomes, treatments, and other risk factors.
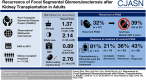
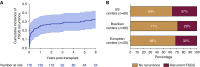
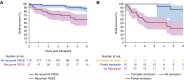
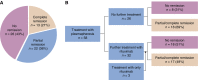
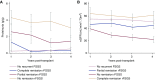
Results: Among 11,742 kidney transplant recipients screened for FSGS, 176 had a diagnosis of idiopathic FSGS and were included. FSGS recurred in 57 patients (32%; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 25% to 39%) and 39% of them lost their graft over a median of 5 (interquartile range, 3.0-8.1) years. Multivariable Cox regression revealed a higher risk for recurrence with older age at native kidney disease onset (hazard ratio [HR], 1.37 per decade; 95% CI, 1.09 to 1.56). Other predictors were white race (HR, 2.14; 95% CI, 1.08 to 4.22), body mass index at transplant (HR, 0.89 per kg/m2; 95% CI, 0.83 to 0.95), and native kidney nephrectomies (HR, 2.76; 95% CI, 1.16 to 6.57). Plasmapheresis and rituximab were the most frequent treatments (81%). Partial or complete remission occurred in 57% of patients and was associated with better graft survival.
Conclusions: Idiopathic FSGS recurs post-transplant in one third of cases and is associated with a five-fold higher risk of graft loss. Response to treatment is associated with significantly better outcomes but is achieved in only half of the cases.
Keywords: Nephrectomy; adult; body mass index; cohort studies; focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; graft survival; humans; incidence; kidney; kidney diseases; kidney transplantation; plasmapheresis; recurrence; registries; renal transplantation; risk factors; rituximab; sample size; transplant outcomes; transplant recipients; treatment outcome.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Facing the Vexing Problem of Recurrent FSGS after Kidney Transplantation.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Feb 7;15(2):171-173. doi: 10.2215/CJN.14841219. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31995516 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Agodoa LY, Albertus P, Ayanian J, Balkrishnan R, Bragg-Gresham J, Cao J, Chen JL, Cope E, Dharmarajan S, Dietrich X, Eckard A, Eggers PW, Gaber C, Gillen D, Gipson D, Gu H, Hailpern SM, Hall YN, Han Y, He K, Hebert H, Helmuth M, Herman W, Heung M, Hutton D, Jacobsen SJ, Ji N, Jin Y, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kapke A, Katz R, Kovesdy CP, Kurtz V, Lavalee D, Li Y, Lu Y, McCullough K, Molnar MZ, Montez-Rath M, Morgenstern H, Mu Q, Mukhopadhyay P, Nallamothu B, Nguyen DV, Norris KC, O’Hare AM, Obi Y, Pearson J, Pisoni R, Plattner B, Port FK, Potukuchi P, Rao P, Ratkowiak K, Ravel V, Ray D, Rhee CM, Schaubel DE, Selewski DT, Shaw S, Shi J, Shieu M, Sim JJ, Song P, Soohoo M, Steffick D, Streja E, Tamura MK, Tentori F, Tilea A, Tong L, Turf M, Wang D, Wang M, Woodside K, Wyncott A, Xin X, Zang W, Zepel L, Zhang S, Zho H, Hirth RA, Shahinian V: US renal data system 2016 annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 69[Suppl 1]: A7–A8, 2017 - PMC - PubMed
-
- D’Agati VD, Kaskel FJ, Falk RJ: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med 365: 2398–2411, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Senggutuvan P, Cameron JS, Hartley RB, Rigden S, Chantler C, Haycock G, Williams DG, Ogg C, Koffman G: Recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in transplanted kidneys: Analysis of incidence and risk factors in 59 allografts. Pediatr Nephrol 4: 21–28, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Banfi G, Colturi C, Montagnino G, Ponticelli C: The recurrence of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in kidney transplant patients treated with cyclosporine. Transplantation 50: 594–596, 1990 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

