Structural instability and divergence from conserved residues underlie intracellular retention of mammalian odorant receptors
- PMID: 31974307
- PMCID: PMC7022149
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1915520117
Structural instability and divergence from conserved residues underlie intracellular retention of mammalian odorant receptors
Abstract
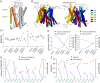
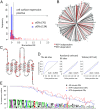
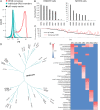
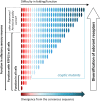
Mammalian odorant receptors are a diverse and rapidly evolving set of G protein-coupled receptors expressed in olfactory cilia membranes. Most odorant receptors show little to no cell surface expression in nonolfactory cells due to endoplasmic reticulum retention, which has slowed down biochemical studies. Here we provide evidence that structural instability and divergence from conserved residues of individual odorant receptors underlie intracellular retention using a combination of large-scale screening of odorant receptors cell surface expression in heterologous cells, point mutations, structural modeling, and machine learning techniques. We demonstrate the importance of conserved residues by synthesizing consensus odorant receptors that show high levels of cell surface expression similar to conventional G protein-coupled receptors. Furthermore, we associate in silico structural instability with poor cell surface expression using molecular dynamics simulations. We propose an enhanced evolutionary capacitance of olfactory sensory neurons that enable the functional expression of odorant receptors with cryptic mutations.
Keywords: GPCR; olfaction; protein trafficking.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: K.I., C.A.d.M., M.H.N., and H.M. filed a provisional patent application relevant to this work. H.M. receives royalties from Chemcom. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

