Genome-scale transcriptional dynamics and environmental biosensing
- PMID: 31974311
- PMCID: PMC7022183
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1913003117
Genome-scale transcriptional dynamics and environmental biosensing
Abstract
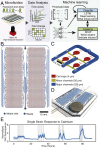
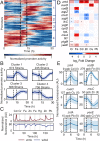
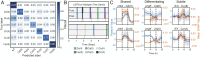
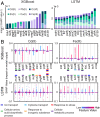
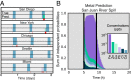
Genome-scale technologies have enabled mapping of the complex molecular networks that govern cellular behavior. An emerging theme in the analyses of these networks is that cells use many layers of regulatory feedback to constantly assess and precisely react to their environment. The importance of complex feedback in controlling the real-time response to external stimuli has led to a need for the next generation of cell-based technologies that enable both the collection and analysis of high-throughput temporal data. Toward this end, we have developed a microfluidic platform capable of monitoring temporal gene expression from over 2,000 promoters. By coupling the "Dynomics" platform with deep neural network (DNN) and associated explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) algorithms, we show how machine learning can be harnessed to assess patterns in transcriptional data on a genome scale and identify which genes contribute to these patterns. Furthermore, we demonstrate the utility of the Dynomics platform as a field-deployable real-time biosensor through prediction of the presence of heavy metals in urban water and mine spill samples, based on the the dynamic transcription profiles of 1,807 unique Escherichia coli promoters.
Keywords: E. coli transcriptomics; biosensor; dynamics; explainable AI; high-throughput microfluidics.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: W.H.M., M.F., S.C., and J.H. have a financial interest in Quantitative BioSciences. Quantitative BioSciences has an exclusive license to IP stemming from this work, which is owned by the University of California San Diego.
Figures
References
-
- Kholodenko B., Yaffe M. B., Kolch W., Computational approaches for analyzing information flow in biological networks. Sci. Signal. 5, re1 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Milo R., et al. , Network motifs: Simple building blocks of complex networks. Science 298, 824–827 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Jacob F., Monod J., Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 3, 318–356 (1961). - PubMed
-
- Gardner T. S., Cantor C. R., Collins J. J., Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature 403, 339–342 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Krupp M., et al. , RNA-Seq Atlas-a reference database for gene expression profiling in normal tissue by next-generation sequencing. Bioinformatics 28, 1184–1185 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

