Intravenous immunoglobulin mediates anti-inflammatory effects in peripheral blood mononuclear cells by inducing autophagy
- PMID: 31974400
- PMCID: PMC6978335
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-2249-y
Intravenous immunoglobulin mediates anti-inflammatory effects in peripheral blood mononuclear cells by inducing autophagy
Abstract
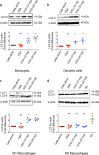
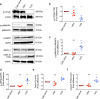
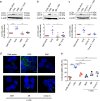
Autophagy plays an important role in the regulation of autoimmune and autoinflammatory responses of the immune cells. Defective autophagy process is associated with various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Moreover, in many of these diseases, the therapeutic use of normal immunoglobulin G or intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), a pooled normal IgG preparation, is well documented. Therefore, we explored if IVIG immunotherapy exerts therapeutic benefits via induction of autophagy in the immune cells. Here we show that IVIG induces autophagy in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Further dissection of this process revealed that IVIG-induced autophagy is restricted to inflammatory cells like monocytes, dendritic cells, and M1 macrophages but not in cells associated with Th2 immune response like M2 macrophages. IVIG induces autophagy by activating AMP-dependent protein kinase, beclin-1, class III phosphoinositide 3-kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and by inhibiting mammalian target of rapamycin. Mechanistically, IVIG-induced autophagy is F(ab')2-dependent but sialylation independent, and requires endocytosis of IgG by innate cells. Inhibition of autophagy compromised the ability of IVIG to suppress the inflammatory cytokines in innate immune cells. Moreover, IVIG therapy in inflammatory myopathies such as dermatomyositis, antisynthetase syndrome and immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy induced autophagy in PBMCs and reduced inflammatory cytokines in the circulation, thus validating the translational importance of these results. Our data provide insight on how circulating normal immunoglobulins maintain immune homeostasis and explain in part the mechanism by which IVIG therapy benefits patients with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin preparation attenuates LPS-induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human monocytic cells by modulating TLR4-mediated signaling pathways.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012 Sep;385(9):891-8. doi: 10.1007/s00210-012-0765-8. Epub 2012 May 31. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22644107
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin induces IL-4 in human basophils by signaling through surface-bound IgE.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Aug;144(2):524-535.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.064. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30529242
-
Heme oxygenase-1 is dispensable for the anti-inflammatory activity of intravenous immunoglobulin.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 22;6:19592. doi: 10.1038/srep19592. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26796539 Free PMC article.
-
[Intravenous immunoglobulin: immunomodulatory key of the immune system].Med Clin (Barc). 2012 Jun 30;139(3):112-7. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2011.11.022. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Med Clin (Barc). 2012. PMID: 22285062 Review. Spanish.
-
Effects of Intravenous Immunoglobulins on Human Innate Immune Cells: Collegium Internationale Allergologicum Update 2024.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2024;185(10):975-996. doi: 10.1159/000539069. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38852585 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of Candida auris and Candida albicans Disseminated Candidiasis.mSphere. 2023 Feb 21;8(1):e0058422. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00584-22. Epub 2023 Jan 23. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 36688668 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Management of Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review.J Pain Res. 2020 Nov 12;13:2879-2884. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S273475. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 33209055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Antibody-Recruiting Molecule Enhances Fcγ Receptor-Mediated Uptake and Killing of Mycobacterial Pathogens by Macrophages.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 13;11(6):1563-1576. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.5c00097. Epub 2025 May 1. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40312277 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed Cell Death Pathways in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 24;12:783616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.783616. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is there a Role of Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Immunologic Recurrent Pregnancy Loss?J Immunol Res. 2020 Dec 27;2020:6672865. doi: 10.1155/2020/6672865. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 33426092 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

