Antipsychotic Treatment Effectiveness in First Episode of Psychosis: PAFIP 3-Year Follow-Up Randomized Clinical Trials Comparing Haloperidol, Olanzapine, Risperidone, Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, and Ziprasidone
- PMID: 31974576
- PMCID: PMC7177160
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa004
Antipsychotic Treatment Effectiveness in First Episode of Psychosis: PAFIP 3-Year Follow-Up Randomized Clinical Trials Comparing Haloperidol, Olanzapine, Risperidone, Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, and Ziprasidone
Abstract
Background: Different effectiveness profiles among antipsychotics may be a key point to optimize treatment in patients suffering a first episode of psychosis to impact on long-term outcome. The aim of this study is to compare the clinical effectiveness of olanzapine, risperidone, haloperidol, aripiprazole, ziprasidone, and quetiapine in the treatment of first episode of psychosis at 3-year follow-up.
Method: From February 2001 to January 2011, 2 phases of a prospective, randomized, open-label study were undertaken. A total of 376 first-episode drug-naïve patients were randomly assigned to olanzapine (n = 55), risperidone (n = 63), haloperidol (n = 56), aripiprazole (n = 78), ziprasidone (n = 62), or quetiapine (n = 62) and followed up for 3 years. The primary effectiveness measure was all cause of treatment discontinuation. In addition, an analysis based on intention-to-treat principle was conducted in the analysis for clinical efficacy.
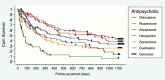
Results: The overall dropout rate at 3 years reached 20.75%. Treatment discontinuation rates were significantly different among treatment groups (olanzapine = 69.09, risperidone = 71.43, aripiprazole = 73.08%, ziprasidone = 79.03%, haloperidol = 89.28%, and quetiapine = 95.53%) (χ2 = 79.86; P = .000). Statistically significant differences in terms of lack of efficacy, adherence, and tolerability were observed among treatment groups along the 3-year follow-up, determining significant differences in time to all-cause discontinuation (log-rank = 92.240; P = .000). Significant differences between treatments were found in the categories of sleepiness/sedation, increased sleep duration, akinesia, weight gain, ejaculatory dysfunction, extrapyramidal-symptoms, and amenorrhea.
Conclusions: Olanzapine, risperidone, and aripiprazole presented advantages for the first-line treatment of first episode of psychosis in terms of effectiveness. Identifying different discontinuation patterns may contribute to optimize treatment selection after first episode of psychosis.ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02526030 https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02526030.
Keywords: antipsychotics; first-episode-psychosis; schizophrenia.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Term Antipsychotic Effectiveness in First Episode of Psychosis: A 3-Year Follow-Up Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Aripiprazole, Quetiapine, and Ziprasidone.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018 Dec 1;21(12):1090-1101. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy082. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30215723 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Incidence and risk factors of acute akathisia in 493 individuals with first episode non-affective psychosis: a 6-week randomised study of antipsychotic treatment.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Sep;234(17):2563-2570. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4646-1. Epub 2017 May 31. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28567698 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of first-episode non-affective psychosis: a randomized comparison of aripiprazole, quetiapine and ziprasidone over 1 year.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Jan;231(2):357-66. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3241-3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 23958945 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of sensitivity and tolerability of antipsychotics in patients with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia: focus on somnolence.J Clin Psychiatry. 2008 Feb;69(2):302-9. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v69n0217. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18211129 Review.
-
An open, large, 6-month naturalistic study of outcome in schizophrenic outpatients, treated with olanzapine.Hum Psychopharmacol. 2011 Jan;26(1):81-5. doi: 10.1002/hup.1173. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 23055416 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical effects of CYP2D6 phenoconversion in patients with psychosis.J Psychopharmacol. 2024 Dec;38(12):1095-1110. doi: 10.1177/02698811241278844. Epub 2024 Sep 23. J Psychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39310932 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Tolerance of Antipsychotics Used for the Treatment of Patients Newly Diagnosed with Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Pharmacy (Basel). 2023 Nov 10;11(6):175. doi: 10.3390/pharmacy11060175. Pharmacy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37987385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five-year trend of antipsychotic prescription practices in a district Hospital in Ghana: A retrospective study.Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2023 Sep;43(3):434-439. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12372. Epub 2023 Aug 13. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37574802 Free PMC article.
-
Aripiprazole vs Risperidone Head-to-Head Effectiveness in First-Episode Non-Affective-Psychosis: A 3-Month Randomized, Flexible-Dose, Open-Label Clinical Trial.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022 Nov 17;25(11):900-911. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyac047. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35894865 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A new synthetic ultrasound-assisted method for dibenzoepines.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 14;9(7):e18319. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18319. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37539205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addington D, Addington J, Maticka-Tyndale E (1993) Assessing depression in schizophrenia: the Calgary depression scale. Br J Psychiatry 163(Suppl 22): 39–44. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen N. (1984) The Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms (SAPS). Iowa City: Univ Iowa.
-
- Andreasen NC. (1989) Scale for the assessment of negative symptoms (SANS). Br J Psychiatry 155:53–58. - PubMed
-
- Asmal L, Flegar SJ, Wang J, Rummel-Kluge C, Komossa K, Leucht S (2013) Quetiapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev Advance online publication. http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/14651858.CD006625.pub3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnes TR. (1989) A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154:672–676. - PubMed