Iron metabolism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 31975563
- PMCID: PMC7378429
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13216
Iron metabolism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Iron metabolism can directly or indirectly affect the occurrence and development of type 2 diabetes. This meta-analysis and systematic review aimed to analyze the association between serum iron metabolism indicators and type 2 diabetes.
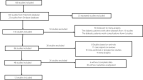
Materials and methods: The databases PubMed and Embase were searched for studies on the correlations between serum iron metabolism indicators (iron, ferritin, transferrin, hepcidin and soluble transferrin receptor) and type 2 diabetes since January 2006. Relevant data were extracted from the included studies, and meta-analysis was carried out.
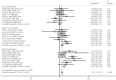
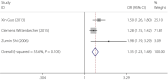
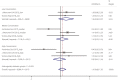
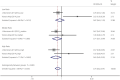
Results: A total of 12 case-control and cohort studies were analyzed. Of the 12 studies, 11 described the correlation between serum ferritin levels and type 2 diabetes. The median and high serum ferritin concentrations were significantly associated with the risks of type 2 diabetes (odds ratio [OR] 1.20, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.08-1.33 and OR 1.43, 95% CI 1.29-1.59, respectively). However, the low concentration was not correlated with the risk of type 2 diabetes (OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.89-1.11). No significant association was observed between serum soluble transferrin receptor and type 2 diabetes, whereas the soluble transferrin receptor-to-ferritin ratio was significantly inversely related to the risk of type 2 diabetes in the median and high ratio subgroups (OR 0.71, 95% CI 0.51, 0.99 and OR 0.65, 95% CI 0.45-0.95).
Conclusions: The elevated serum ferritin was one of the risk factors for type 2 diabetes, and soluble transferrin receptor-to-ferritin ratio was inversely related to the risk of type 2 diabetes. A systematic review showed that serum transferrin and hepcidin might be directly or indirectly related to the development of diabetes.
Keywords: Ferritin; Soluble transferrin receptor; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Relationship between soluble transferrin receptor and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis.J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Jun;12(6):1118-1119. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13442. Epub 2020 Nov 18. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. PMID: 33205583 Free PMC article.
-
Response to "Relationship between soluble transferrin receptor and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis".J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Jun;12(6):1120-1121. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13505. Epub 2021 Feb 20. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. PMID: 33608979 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Xu Y, Wang L, He J, et al Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA 2013; 310: 948–959. - PubMed
-
- Fernández‐Real JM, Ricart‐Engel W, Arroyo E, et al Serum ferritin as a component of the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes Care 1998; 21: 62–68. - PubMed
-
- Wilson JG, Lindquist JH, Grambow SC, et al Potential role of increased iron stores in diabetes. Am J Med Sci 2003; 325: 332–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

