Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Is Superior to Plate Fixation at 2 Years for Displaced Proximal Humeral Fractures in the Elderly: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 31977825
- PMCID: PMC7508281
- DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.19.01071
Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Is Superior to Plate Fixation at 2 Years for Displaced Proximal Humeral Fractures in the Elderly: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Is Superior to Plate Fixation at 2 Years for Displaced Proximal Humeral Fractures in the Elderly.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020 Jun 17;102(12):e63. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ER.19.01071. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020. PMID: 32555037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Almost one-third of patients with proximal humeral fractures are treated surgically, and the number is increasing. When surgical treatment is chosen, there is sparse evidence on the optimum method. The DelPhi (Delta prosthesis-PHILOS plate) trial is a clinical trial comparing 2 surgical treatments. Our hypothesis was that reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) yields better clinical results compared with open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) using an angular stable plate.
Methods: The DelPhi trial is a randomized controlled trial comparing reverse TSA with ORIF for displaced proximal humeral fractures (OTA/AO types 11-B2 and 11-C2) in elderly patients (65 to 85 years of age). The primary outcome measure was the Constant score at a 2-year follow-up. The secondary outcome measures included the Oxford Shoulder Score and radiographic evaluation. Results were reported as the mean difference with 95% confidence interval (CI). The intention-to-treat principle was applied for crossover patients.
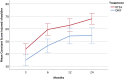
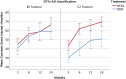
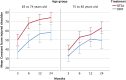
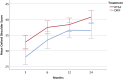
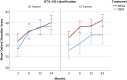
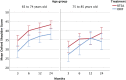
Results: There were 124 patients included in the study. At 2 years, the mean Constant score was 68.0 points (95% CI, 63.7 to 72.4 points) for the reverse TSA group compared with 54.6 points (95% CI, 48.5 to 60.7 points) for the ORIF group, resulting in a significant mean difference of 13.4 points (95% CI, 6.2 to 20.6 points; p < 0.001) in favor of reverse TSA. When stratified for fracture classification, the mean score was 69.3 points (95% CI, 63.9 to 74.7 points) for the reverse TSA group and 50.6 points (95% CI, 41.9 to 59.2 points) for the ORIF group for type-C2 fractures, which yielded a significant mean difference of 18.7 points (95% CI, 9.3 to 28.2 points; p < 0.001). In the type-B2 fracture group, the mean score was 66.2 points (95% CI, 58.6 to 73.8 points) for the reverse TSA group and 58.5 points (95% CI, 49.6 to 67.4 points) for the ORIF group, resulting in a nonsignificant mean difference of 7.6 points (95% CI, -3.8 to 19.1 points; p = 0.19).
Conclusions: At a 2-year follow-up, the data suggested an advantage of reverse TSA over ORIF in the treatment of displaced OTA/AO type-B2 and C2 proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients.
Level of evidence: Therapeutic Level I. See Instructions for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures
Comment in
-
A Word of Caution: Success May Be Limited to 2 Years and Highly Displaced OTA/AO B2 and C2 Injuries: Commentary on an article by Alexander Nilsskog Fraser, MD, et al.: "Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Is Superior to Plate Fixation at 2 Years for Displaced Proximal Humeral Fractures in the Elderly. A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial".J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020 Mar 18;102(6):e30. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.19.01475. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020. PMID: 32195741 No abstract available.
References
-
- Court-Brown CM, Garg A, McQueen MM. The epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001. August;72(4):365-71. - PubMed
-
- Fjalestad T, Hole MO, Jørgensen JJ, Strømsøe K, Kristiansen IS. Health and cost consequences of surgical versus conservative treatment for a comminuted proximal humeral fracture in elderly patients. Injury. 2010. June;41(6):599-605. Epub 2009 Nov 27. - PubMed
-
- Handoll H, Brealey S, Rangan A, Keding A, Corbacho B, Jefferson L, Chuang LH, Goodchild L, Hewitt C, Torgerson D. The ProFHER (PROximal Fracture of the Humerus: Evaluation by Randomisation) trial - a pragmatic multicentre randomised controlled trial evaluating the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of surgical compared with non-surgical treatment for proximal fracture of the humerus in adults. Health Technol Assess. 2015. March;19(24):1-280. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Han RJ, Sing DC, Feeley BT, Ma CB, Zhang AL. Proximal humerus fragility fractures: recent trends in nonoperative and operative treatment in the Medicare population. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016. February;25(2):256-61. Epub 2015 Oct 2. - PubMed
-
- Fjalestad T, Hole MO, Hovden IA, Blücher J, Strømsøe K. Surgical treatment with an angular stable plate for complex displaced proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2012. February;26(2):98-106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

