HIV RNA measurement in dried blood spots of HIV-infected patients in Thailand using Abbott m2000 system
- PMID: 31978113
- PMCID: PMC6980635
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227929
HIV RNA measurement in dried blood spots of HIV-infected patients in Thailand using Abbott m2000 system
Abstract
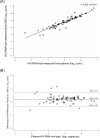
World Health Organization recommends using dried blood spots (DBS) for HIV RNA viral load (VL) measurement whenever plasma processing is not convenient or feasible. DBS collected from 80 treatment-naïve HIV-infected patients presenting in three hospitals of two different regions of Thailand were shipped to a central laboratory along with corresponding plasma specimens. Viral load was measured in both DBS and plasma using the Abbott m2000 system. HIV RNA levels were strongly correlated (r = 0.94) with a mean of differences of 0.23 log10 copies/mL. Using the 1,000 copies/mL cut-off, the sensitivity of DBS was 97% (95%CI, 91-100%) and specificity was 75% (95%CI, 19-99%). DBS are useful to scale-up HIV RNA VL testing in settings with limited access to VL testing.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. Fast-Track: ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030. Geneva, Switzerland: The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2014.
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. 90-90-90 On the right track towards the global target Geneva, Switzerland: The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2016.
-
- National Health Security Office. National Health Security Fund Management Manual Volume 2 Management of HIV / AIDS Service Accounts and Management of Tuberculosis Patients (in Thai). Bangkok, Thailand: National Health Security Office; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical