Hematological factors associated with immunity, inflammation, and metabolism in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Data from a Zhuang cohort in Southwest China
- PMID: 31978275
- PMCID: PMC7307337
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23211
Hematological factors associated with immunity, inflammation, and metabolism in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Data from a Zhuang cohort in Southwest China
Abstract
Introduction: Hematological parameters play important role in multiple diseases. This study was to investigate the possible association of the routine hematological parameters involved in immunity, inflammation, and metabolism with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in patients of Zhuang ethnicity in Guangxi, southwest China.
Methods: The medical records of 195 Zhuang SLE patients between January 2013 and November 2018 were retrospectively reviewed. Random forest algorithm and multivariate logistic regression were used to identify the feature hematological parameters in patients with SLE. Association rules were explored between each parameter and immunity- (IgG, IgA, IgM, C3, and C4), inflammation- (ESR, hs-CRP, and CAR), and metabolism- (TG, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, TP, PA, ALB, and UA) related indexes.
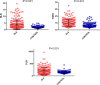
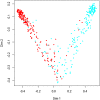
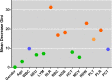
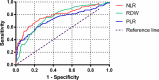
Results: Random forest algorithm and logistic regression analysis showed that neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), red blood cell distribution width (RDW), and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were the feature parameters for distinguishing SLE patients from healthy controls. According to the ROC curves, the optimal cutoff values to predict SLE were 1.98 for NLR, 13.35 for RDW, and 145.64 for PLR. Association rule analysis showed that NLR was strongly associated with C3, hs-CRP, TG, ALB, and UA; RDW was strongly associated with C3, C4, hs-CRP, TG, and ALB; PLR was strongly associated with IgG, hs-CRP, HDL-C, and UA.
Conclusions: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, RDW, and PLR may serve as effective predictors of dysregulation in immunity, inflammation, and metabolism. These three indicators may be potential for cardiovascular risk assessment in Zhuang SLE patients in southwest China.
Keywords: association rule; hematological parameters; immunity; inflammation; metabolism; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were useful markers in assessment of inflammatory response and disease activity in SLE patients.Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(3):372-6. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1091136. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Mod Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26403379
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were associated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Jul;36:94-99. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27111516
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratios in systemic lupus erythematosus: Relation with disease activity and lupus nephritis.Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2020 Jul-Aug;16(4):255-261. doi: 10.1016/j.reuma.2018.07.008. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2020. PMID: 30166230 English, Spanish.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jul 25;24(1):170. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01438-5. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39052098 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a biomarker of systemic inflammation in systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis and systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 May 16;19(5):e0303665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303665. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38753735 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Changes in routine blood parameters of patients with generalized tonic clonic seizure: a retrospective study.Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2023 Apr;28(2):123-129. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2023.2.20220135. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2023. PMID: 37045465 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Serum Interleukin 10 Levels Are Associated with Increased Disease Activity and Increased Risk of Anti-SS-A/Ro Antibody Positivity in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 11;13(6):974. doi: 10.3390/biom13060974. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371554 Free PMC article.
-
Do not exclude your observations: Negative cortisol awakening responses (CAR) may be biologically relevant.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2025 May;175:107417. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2025.107417. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2025. PMID: 40023887
-
Study the Mechanism of Gualou Niubang Decoction in Treating Plasma Cell Mastitis Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jun 15;2022:5780936. doi: 10.1155/2022/5780936. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35757473 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Prognostic Nutritional Indexes and the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 Jun 12;18:1155-1167. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S402717. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 37332836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia Tello A, Villegas Martinez A, Gonzalez Fernandez AF. Hematological abnormalities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. An Med Interna. 2002;19(10):539‐543. - PubMed
-
- Urowitz MB, Bookman AAM, Koehler BE, et al. The bimodal mortality pattern of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1976;60(2):221‐225. - PubMed
-
- Manzi S, Meilahn EN, Rairie JE, et al. Age‐specific incidence rates of myocardial infarction and angina in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: comparison with the Framingham Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;145(5):408‐415. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

