Predicting the Associations between Meridians and Chinese Traditional Medicine Using a Cost-Sensitive Graph Convolutional Neural Network
- PMID: 31979314
- PMCID: PMC7036907
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17030740
Predicting the Associations between Meridians and Chinese Traditional Medicine Using a Cost-Sensitive Graph Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
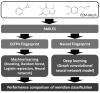
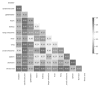
Natural products are the most important and commonly used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for healthcare and disease prevention in East-Asia. Although the Meridian system of TCM was established several thousand years ago, the rationale of Meridian classification based on the ingredient compounds remains poorly understood. A core challenge for the traditional machine learning approaches for chemical activity prediction is to encode molecules into fixed length vectors but ignore the structural information of the chemical compound. Therefore, we apply a cost-sensitive graph convolutional neural network model to learn local and global topological features of chemical compounds, and discover the associations between TCM and their Meridians. In the experiments, we find that the performance of our approach with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC-AUC) of 0.82 which is better than the traditional machine learning algorithm and also obtains 8%-13% improvement comparing with the state-of-the-art methods. We investigate the powerful ability of deep learning approach to learn the proper molecular descriptors for Meridian prediction and to provide novel insights into the complementary and alternative medicine of TCM.
Keywords: Meridian classification; Traditional Chinese Medicine; graph convolutional neural network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest and the funders had no role in the design of the study.
Figures
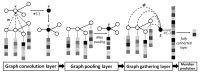
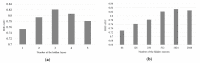
Similar articles
-
Multi-target meridians classification based on the topological structure of anti-cancer phytochemicals using deep learning.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 2):117244. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117244. Epub 2023 Sep 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37777031
-
Predicting Meridian in Chinese traditional medicine using machine learning approaches.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Nov 25;15(11):e1007249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007249. eCollection 2019 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31765369 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-drug interaction prediction of traditional Chinese medicine based on graph attention networks.Sci Rep. 2025 May 28;15(1):18635. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00725-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40436979 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Traditional Chinese Medicine Glossary of Meridian Pathways and Its English Translations.Altern Ther Health Med. 2022 Feb;28(2):50-57. Altern Ther Health Med. 2022. PMID: 32088677 Review.
-
[Research progress on meridian-guiding theory of traditional Chinese medicine].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Jul;41(13):2428-2434. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20161310. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28905564 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Use of Artificial Intelligence in Complementary and Alternative Medicine: A Systematic Scoping Review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 1;13:826044. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.826044. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35431917 Free PMC article.
-
AI empowering traditional Chinese medicine?Chem Sci. 2024 Sep 23;15(41):16844-86. doi: 10.1039/d4sc04107k. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39355231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infant Low Birth Weight Prediction Using Graph Embedding Features.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 11;20(2):1317. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021317. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36674072 Free PMC article.
-
Digital intelligence technology: new quality productivity for precision traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1526187. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1526187. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40264673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Improved Deep Learning Model: S-TextBLCNN for Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula Classification.Front Genet. 2021 Dec 22;12:807825. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.807825. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 35003231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng J.T. Herbal Medicines. Volume 604. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2016. Chinese Herbal Medicine: Perspectives; pp. 225–235.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

