In situ antibody phage display yields optimal inhibitors of integrin α11/β1
- PMID: 31980006
- PMCID: PMC6999838
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2020.1717265
In situ antibody phage display yields optimal inhibitors of integrin α11/β1
Abstract
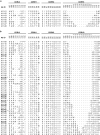
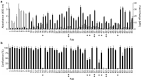
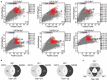
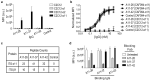
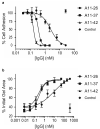
Integrins are transmembrane multi-conformation receptors that mediate interactions with the extracellular matrix. In cancer, integrins influence metastasis, proliferation, and survival. Collagen-binding integrin-α11/β1, a marker of aggressive tumors that is involved in stroma-tumor crosstalk, may be an attractive target for anti-cancer therapeutic antibodies. We performed selections with phage-displayed synthetic antibody libraries for binding to either purified integrin-α11/β1 or in situ on live cells. The in-situ strategy yielded many diverse antibodies, and strikingly, most of these antibodies did not recognize purified integrin-α11/β1. Conversely, none of the antibodies selected for binding to purified integrin-α11/β1 were able to efficiently recognize native cell-surface antigen. Most importantly, only the in-situ selection yielded functional antibodies that were able to compete with collagen-I for binding to cell-surface integrin-α11/β1, and thus inhibited cell adhesion. In-depth characterization of a subset of in situ-derived clones as full-length immunoglobulins revealed high affinity cellular binding and inhibitory activities in the single-digit nanomolar range. Moreover, the antibodies showed high selectivity for integrin-α11/β1 with minimal cross-reactivity for close homologs. Taken together, our findings highlight the advantages of in-situ selections for generation of anti-integrin antibodies optimized for recognition and inhibition of native cell-surface proteins, and our work establishes general methods that could be extended to many other membrane proteins.
Keywords: Enhanced diversity; ITGA11; antibody selections; cancer therapeutics; cellular selections; integrin-α11/β1 receptor.
Figures
References
-
- Hood JD, Cheresh DA. Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat Rev Cancer [Internet]. 2002. [accessed 2019 November18];2:91–100. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12635172. - PubMed
-
- Cabodi S, Moro L, Bergatto E, Boeri Erba E, Di Stefano P, Turco E, Tarone G, Defilippi P. Integrin regulation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and of EGF-dependent responses. Biochem Soc Trans [Internet]. 2004. [accessed 2016 February20];32:438–42. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15157155. - PubMed
-
- Montresor A, Bolomini-Vittori M, Toffali L, Rossi B, Constantin G, Laudanna C. JAK tyrosine kinases promote hierarchical activation of Rho and Rap modules of integrin activation. J Cell Biol [Internet]. 2013. [accessed 2016 February20];203:1003–19. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3871442&tool=p.... - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eberwein P, Laird D, Schulz S, Reinhard T, Steinberg T, Tomakidi P. Modulation of focal adhesion constituents and their down-stream events by EGF: on the cross-talk of integrins and growth factor receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta, Mol Cell Res [Internet]. 2015. [accessed 2016 January9];1853:2183–98. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26079101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
