Cellular and molecular basis of liver regeneration
- PMID: 31980376
- PMCID: PMC7108750
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.12.004
Cellular and molecular basis of liver regeneration
Abstract
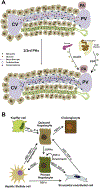
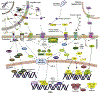
Recent advances in genetics and genomics have reinvigorated the field of liver regeneration. It is now possible to combine lineage-tracing with genome-wide studies to genetically mark individual liver cells and their progenies and detect precise changes in their genome, transcriptome, and proteome under normal versus regenerative settings. The recent use of single-cell RNA sequencing methodologies in model organisms has, in some ways, transformed our understanding of the cellular and molecular biology of liver regeneration. Here, we review the latest strides in our knowledge of general principles that coordinate regeneration of the liver and reflect on some conflicting evidence and controversies surrounding this topic. We consider the prominent mechanisms that stimulate homeostasis-related vis-à-vis injury-driven regenerative responses, highlight the likely cellular sources/depots that reconstitute the liver following various injuries and discuss the extrinsic and intrinsic signals that direct liver cells to proliferate, de-differentiate, or trans-differentiate while the tissue recovers from acute or chronic damage.
Keywords: Hepatocellular plasticity; Lineage-tracing; Liver injury and repair; Single-cell RNA sequencing; Transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Michalopoulos GK & DeFrances MC Liver regeneration. Science 276, 60–66 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Si-Tayeb K, Lemaigre FP & Duncan SA Organogenesis and development of the liver. Dev. Cell 18, 175–189 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Vilarinho S & Lifton RP Liver transplantation: from inception to clinical practice. Cell 150, 1096–1099 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

