Regulatory T-cell therapy in Crohn's disease: challenges and advances
- PMID: 31980447
- PMCID: PMC7229901
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319850
Regulatory T-cell therapy in Crohn's disease: challenges and advances
Abstract
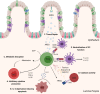
The prevalence of IBD is rising in the Western world. Despite an increasing repertoire of therapeutic targets, a significant proportion of patients suffer chronic morbidity. Studies in mice and humans have highlighted the critical role of regulatory T cells in immune homeostasis, with defects in number and suppressive function of regulatory T cells seen in patients with Crohn's disease. We review the function of regulatory T cells and the pathways by which they exert immune tolerance in the intestinal mucosa. We explore the principles and challenges of manufacturing a cell therapy, and discuss clinical trial evidence to date for their safety and efficacy in human disease, with particular focus on the development of a regulatory T-cell therapy for Crohn's disease.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; T lymphocytes; immunology; immunoregulation; intestinal T cells.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: PMI is the Chief Investigator and GML is the Chief Scientific Investigator on the Medical Research Council-funded TRIBUTE trial of Treg immunotherapy in CD (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03185000).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
