Adjuvant therapy for grade 3, deeply invasive endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the uterus
- PMID: 31980487
- PMCID: PMC8270113
- DOI: 10.1136/ijgc-2019-000807
Adjuvant therapy for grade 3, deeply invasive endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the uterus
Abstract
Background: Patients with grade 3, deeply invasive endometrioid adenocarcinoma are typically managed with primary surgery. The role and type of adjuvant therapy used is controversial. We sought to evaluate the role of adjuvant radiation and/or chemotherapy in women with deeply invasive grade 3 endometrioid tumors.
Methods: A multi-center retrospective chart review was performed at three large medical institutions in the United States. Patients with grade 3 endometrioid adenocarcinoma invading >50% of the myometrium were included. Medical records were queried to evaluate whether lymph node assessment was performed, the status of the lymph nodes, adjuvant treatment strategy used, and dates of death or recurrence.
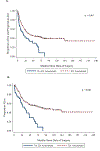
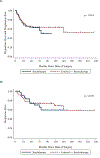
Results: Between 1984 and 2013, 257 patients were identified with a median follow-up of 3.08 years. Most patients (84.7%) had evaluation of pelvic and/or para-aortic lymph nodes and 43% had positive lymph nodes. For node negative patients, there was no difference in overall survival (OS) between those who received adjuvant pelvic radiation +/- vaginal brachytherapy (n=52) vs brachytherapy alone (n=46) (5-year probabilities were 0.73 vs 0.70, P=0.729). Among patients with positive lymph nodes (n=92), the adjuvant treatment strategy utilized impacted OS, with women undergoing a combination of chemotherapy and external beam radiation having the best outcomes (P=0.003).
Conclusions: Among women with grade 3, deeply invasive endometrioid adenocarcinoma, vaginal cuff brachytherapy alone resulted in similar survival when compared with pelvic radiation in node negative patients. The combination of chemotherapy with external beam radiation was associated with improved OS for women with positive nodes.
Keywords: endometrial neoplasms; lymph nodes; pathology; radiotherapy.
© IGCS and ESGO 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–E386. - PubMed
-
- Aalders J, Abeler V, Kolstad P, et al.: Post- operative external irradiation and prognostic pa- rameters in stage I endometrial carcinoma: Clin- ical and histopathologic study of 540 patients. Obstet Gynecol 56:419–427, 1980 - PubMed
-
- Rasool N, Nickles Fader A, Seamon L, Neubauer NL, Abu Shahin F, Alexander HA, Moore K, Moxley K, Alvarez Secord A, Kunos C, Rose PG, O’Malley DM. Stage I, grade 3 endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the endometrium: An analysis of clinical outcomes and patterns of recurrence. Gyn Onc, 2010: 116:1, 10–14. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Uterine Cancer (Version 4.2019). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/uterine.pdf. Accessed October 17, 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

