ECM1 is an essential factor for the determination of M1 macrophage polarization in IBD in response to LPS stimulation
- PMID: 31980528
- PMCID: PMC7022174
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1912774117
ECM1 is an essential factor for the determination of M1 macrophage polarization in IBD in response to LPS stimulation
Abstract
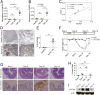
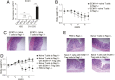
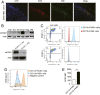
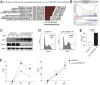
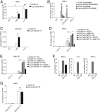
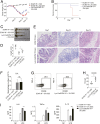
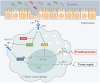
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) comprises chronic relapsing disorders of the gastrointestinal tract characterized pathologically by intestinal inflammation and epithelial injury. Here, we uncover a function of extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) in promoting the pathogenesis of human and mouse IBD. ECM1 was highly expressed in macrophages, particularly tissue-infiltrated macrophages under inflammatory conditions, and ECM1 expression was significantly induced during IBD progression. The macrophage-specific knockout of ECM1 resulted in increased arginase 1 (ARG1) expression and impaired polarization into the M1 macrophage phenotype after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment. A mechanistic study showed that ECM1 can regulate M1 macrophage polarization through the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor/STAT5 signaling pathway. Pathological changes in mice with dextran sodium sulfate-induced IBD were alleviated by the specific knockout of the ECM1 gene in macrophages. Taken together, our findings show that ECM1 has an important function in promoting M1 macrophage polarization, which is critical for controlling inflammation and tissue repair in the intestine.
Keywords: ARG1; ECM1; GM-CSF; IBD; STAT5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Deckers M. M., et al. , Recombinant human extracellular matrix protein 1 inhibits alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization of mouse embryonic metatarsals in vitro. Bone 28, 14–20 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Hamada T., et al. , Lipoid proteinosis maps to 1q21 and is caused by mutations in the extracellular matrix protein 1 gene (ECM1). Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 833–840 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

