Dialysis facility referral and start of evaluation for kidney transplantation among patients treated with dialysis in the Southeastern United States
- PMID: 31981441
- PMCID: PMC10204587
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15791
Dialysis facility referral and start of evaluation for kidney transplantation among patients treated with dialysis in the Southeastern United States
Abstract
Variability in transplant access exists, but barriers to referral and evaluation are underexplored due to lack of national surveillance data. We examined referral for kidney transplantation evaluation and start of the evaluation among 34 857 incident, adult (18-79 years) end-stage kidney disease patients from 690 dialysis facilities in the United States Renal Data System from January 1, 2012 through August 31, 2016, followed through February 2018 and linked data to referral and evaluation data from nine transplant centers in Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina. Multivariable-adjusted competing risk analysis examined each outcome. The median within-facility cumulative percentage of patients referred for kidney transplantation within 1 year of dialysis at the 690 dialysis facilities in Network 6 was 33.7% (interquartile range [IQR]: 25.3%-43.1%). Only 48.3% of referred patients started the transplant evaluation within 6 months of referral. In multivariable analyses, factors associated with referral vs evaluation start among those referred at any time differed. For example, black, non-Hispanic patients had a higher rate of referral (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.22; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.18-1.27), but lower evaluation start among those referred (HR: 0.93; 95% CI: 0.88-0.98), vs white non-Hispanic patients. Barriers to transplant varied by step, and national surveillance data should be collected on early transplant steps to improve transplant access.
Keywords: clinical research/practice; dialysis; disparities; epidemiology; ethnicity/race; health services and outcomes research; kidney transplantation/nephrology; patient referral.
© 2020 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures
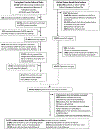
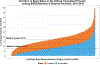
References
-
- United States Renal Data System. 2018 USRDS annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2018.
-
- Department of Health and Human Services. Medicare Program; End-Stage Renal Disease Prospective Payment System, Payment for Renal Dialysis Services Furnished to Individuals with Acute Kidney Injury, End-Stage Renal Disease Quality Incentive Program. In: Services CfMaM, ed. Washington, DC: 2018. - PubMed

