R-Roscovitine Improves Motoneuron Function in Mouse Models for Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- PMID: 31981925
- PMCID: PMC6992996
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.100826
R-Roscovitine Improves Motoneuron Function in Mouse Models for Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Abstract
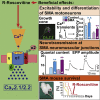
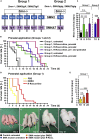
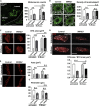
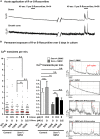
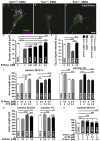
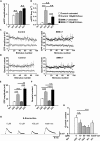
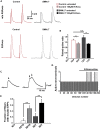
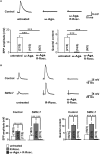
Neurotransmission defects and motoneuron degeneration are hallmarks of spinal muscular atrophy, a monogenetic disease caused by the deficiency of the SMN protein. In the present study, we show that systemic application of R-Roscovitine, a Cav2.1/Cav2.2 channel modifier and a cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk-5) inhibitor, significantly improved survival of SMA mice. In addition, R-Roscovitine increased Cav2.1 channel density and sizes of the motor endplates. In vitro, R-Roscovitine restored axon lengths and growth cone sizes of Smn-deficient motoneurons corresponding to enhanced spontaneous Ca2+ influx and elevated Cav2.2 channel cluster formations independent of its capability to inhibit Cdk-5. Acute application of R-Roscovitine at the neuromuscular junction significantly increased evoked neurotransmitter release, increased the frequency of spontaneous miniature potentials, and lowered the activation threshold of silent terminals. These data indicate that R-Roscovitine improves Ca2+ signaling and Ca2+ homeostasis in Smn-deficient motoneurons, which is generally crucial for motoneuron differentiation, maturation, and function.
Keywords: Cellular Neuroscience; Clinical Neuroscience; Neuroscience.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Balezina O.P., Bogacheva P.O., Orlova T.Y. Effect of L-type calcium channel blockers on activity of newly formed synapses in mice. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007;143:171–174. - PubMed
-
- Biondi O., Grondard C., Lecolle S., Deforges S., Pariset C., Lopes P., Cifuentes-Diaz C., Li H., della G.B., Chanoine C., Charbonnier F. Exercise-induced activation of NMDA receptor promotes motor unit development and survival in a type 2 spinal muscular atrophy model mouse. J. Neurosci. 2008;28:953–962. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biondi O., Branchu J., Sanchez G., Lancelin C., Deforges S., Lopes P., Pariset C., Lecolle S., Cote J., Chanoine C., Charbonnier F. In vivo NMDA receptor activation accelerates motor unit maturation, protects spinal motor neurons, and enhances SMN2 gene expression in severe spinal muscular atrophy mice. J. Neurosci. 2010;30:11288–11299. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruyere C., Meijer L. Targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in anti-neoplastic therapy. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013;25:772–779. - PubMed
-
- Buraei Z., Elmslie K.S. The separation of antagonist from agonist effects of trisubstituted purines on CaV2.2 (N-type) channels. J. Neurochem. 2008;105:1450–1461. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

