Imaging epilepsy in larval zebrafish
- PMID: 31982307
- PMCID: PMC7035958
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2020.01.006
Imaging epilepsy in larval zebrafish
Abstract
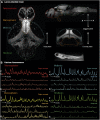
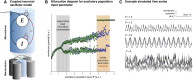
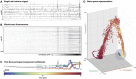
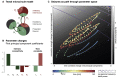
Our understanding of the genetic aetiology of paediatric epilepsies has grown substantially over the last decade. However, in order to translate improved diagnostics to personalised treatments, there is an urgent need to link molecular pathophysiology in epilepsy to whole-brain dynamics in seizures. Zebrafish have emerged as a promising new animal model for epileptic seizure disorders, with particular relevance for genetic and developmental epilepsies. As a novel model organism for epilepsy research they combine key advantages: the small size of larval zebrafish allows high throughput in vivo experiments; the availability of advanced genetic tools allows targeted modification to model specific human genetic disorders (including genetic epilepsies) in a vertebrate system; and optical access to the entire central nervous system has provided the basis for advanced microscopy technologies to image structure and function in the intact larval zebrafish brain. There is a growing body of literature describing and characterising features of epileptic seizures and epilepsy in larval zebrafish. Recently genetically encoded calcium indicators have been used to investigate the neurobiological basis of these seizures with light microscopy. This approach offers a unique window into the multiscale dynamics of epileptic seizures, capturing both whole-brain dynamics and single-cell behaviour concurrently. At the same time, linking observations made using calcium imaging in the larval zebrafish brain back to an understanding of epileptic seizures largely derived from cortical electrophysiological recordings in human patients and mammalian animal models is non-trivial. In this review we briefly illustrate the state of the art of epilepsy research in zebrafish with particular focus on calcium imaging of epileptic seizures in the larval zebrafish. We illustrate the utility of a dynamic systems perspective on the epileptic brain for providing a principled approach to linking observations across species and identifying those features of brain dynamics that are most relevant to epilepsy. In the following section we survey the literature for imaging features associated with epilepsy and epileptic seizures and link these to observations made from humans and other more traditional animal models. We conclude by identifying the key challenges still facing epilepsy research in the larval zebrafish and indicate strategies for future research to address these and integrate more directly with the themes and questions that emerge from investigating epilepsy in other model systems and human patients.
Keywords: Calcium imaging; Dynamical systems; Epilepsy; Genetic epilepsies; Zebrafish.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest No other relevant affiliations or conflicts of interest are declared by any of the authors. ÉS a Co-Founder of Modelis inc. SCB is Co-Founder and Scientific Advisory Board member for Epygenix Therapeutics; and Scientific Advisory Board member for ZeClinics.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas R.H., Berkovic S.F. The hidden genetics of epilepsy—a clinically important new paradigm. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014;10(5):283–292. - PubMed
-
- Berkovic S.F. Epilepsy research in 2016: new treatment directions. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(1):7–9. - PubMed
-
- McTague A., Howell K.B., Cross J.H., Kurian M.A., Scheffer I.E. The genetic landscape of the epileptic encephalopathies of infancy and childhood. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(3):304–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

