A recombinant infectious bronchitis virus from a chicken with a spike gene closely related to that of a turkey coronavirus
- PMID: 31982944
- PMCID: PMC7087231
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-019-04488-3
A recombinant infectious bronchitis virus from a chicken with a spike gene closely related to that of a turkey coronavirus
Abstract
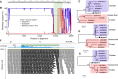
Using viral metagenomics, the complete genome sequence of an infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) strain (named ahysx-1) from a fecal sample from a healthy chicken in Anhui province, China, was determined. The genome sequence of ahysx-1 was found to be very similar to that of IBV strain ck/CH/LLN/131040 (KX252787), except for the spike gene region, which is similar to that of a turkey coronavirus strain (EU022526), suggesting that ahysx-1 is a recombinant. Recombination analysis and phylogenetic analysis based on the genomic sequences of ahysx-1 and other related strains confirmed that ahysx-1 appears to be a recombinant resulting from a recombination event that occurred between a chicken coronavirus and a turkey coronavirus. Further studies need to be performed to determine whether this recombinant IBV strain is pathogenic and whether it is transmitted between chickens and turkeys.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Genome recombination; Infectious bronchitis virus; Viral metagenomics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Woo PCY, Lau SKP, Lam CSF, et al. Discovery of Seven Novel Mammalian and Avian Coronaviruses in the Genus Deltacoronavirus Supports Bat Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and Avian Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. J Virol. 2012;86:3995–4008. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06540-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ziebuhr J, Thiel V, Gorbalenya AE. The autocatalytic release of a putative RNA virus transcription factor from its polyprotein precursor involves two paralogous papain-like proteases that cleave the same peptide bond. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:33220–33232. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104097200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017YFC1200201/National Key Research and Development Programs of China
- BE2017693/Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Projects
- 81741062/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 201810299587W/Student's Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program
- No/Blood Systems Research Institute
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

