The WORD: Outcomes of a Behavioral Weight Loss Maintenance Effectiveness Trial in Rural Black Adults of Faith
- PMID: 31984668
- PMCID: PMC7042080
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.22717
The WORD: Outcomes of a Behavioral Weight Loss Maintenance Effectiveness Trial in Rural Black Adults of Faith
Abstract
Objective: Rural black communities bear a disproportionate burden of obesity. To increase reach among underserved groups, community-based weight loss and maintenance interventions are crucial.
Methods: The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) was adapted for rural black adults of faith to create The Wholeness, Oneness, Righteousness, Deliverance (WORD) trial, a group-based, community health worker-delivered weight loss intervention. A Weight Loss Only arm (16 sessions) was compared with a Weight Loss + Maintenance arm (16 + 12 sessions) in a cluster randomized controlled trial of 31 churches (n = 440). Weight and related behaviors were assessed at 0, 6, 12, and 18 months.
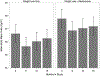
Results: The WORD produced weight loss from baseline to 6 months (percentage body weight change -2.47 [-3.13 to -1.80]). Among those who lost 5% of their baseline weight, there was a statistical trend of lower weight regain in the Weight Loss + Maintenance arm compared with control. Maintenance arm participants reported higher activity at 12 months. There were no between-arm differences at 18 months.
Conclusions: The WORD produced weight loss from baseline to 6 months on par with that produced by other DPP adaptations for black communities, including adaptations using health professionals. Weight regain was also consistent with that reported in prior literature. Continuing sessions as part of the church's mission may foster adoption of DPP-based weight loss programs.
© 2020 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2002;288(14):1723–1727. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Flegal KM. Prevalence of Obesity Among Adults and Youth: United States, 2011–2014. NCHS Data Brief. 2015(219):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Franz MJ, Boucher JL, Rutten-Ramos S, VanWormer JJ. Lifestyle weight-loss intervention outcomes in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015;115(9):1447–1463. - PubMed
-
- Appel LJ, Champagne CM, Harsha DW, et al. Effects of comprehensive lifestyle modification on blood pressure control: main results of the PREMIER clinical trial. Jama. 2003;289(16):2083–2093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

