Results of the 2018 Rapid DNA Maturity Assessment
- PMID: 31985834
- PMCID: PMC11034630
- DOI: 10.1111/1556-4029.14267
Results of the 2018 Rapid DNA Maturity Assessment
Abstract
Three commercially available integrated rapid DNA instruments were tested as a part of a rapid DNA maturity assessment in July of 2018. The assessment was conducted with sets of blinded single-source reference samples provided to participants for testing on the individual rapid platforms within their laboratories. The data were returned to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) for review and analysis. Both FBI-defined automated review (Rapid DNA Analysis) and manual review (Modified Rapid DNA Analysis) of the datasets were conducted to assess the success of genotyping the 20 Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) core STR loci and full profiles generated by the instruments. Genotype results from the multiple platforms, participating laboratories, and STR typing chemistries were combined into a single analysis. The Rapid DNA Analysis resulted in a success rate of 80% for full profiles (85% for the 20 CODIS core loci) with automated analysis. Modified Rapid DNA Analysis resulted in a success rate of 90% for both the CODIS 20 core loci and full profiles (all attempted loci per chemistry). An analysis of the peak height ratios demonstrated that 95% of all heterozygous alleles were above 59% heterozygote balance. For base-pair sizing precision, the precision was below the standard 0.5 bp deviation for both the ANDE 6C System and the RapidHIT 200.
Keywords: ANDE 6C; FlexPlex; GlobalFiler; RapidHIT 200; RapidHIT ID; integrated device; rapid DNA.
Published 2020. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
Julie French is an employee and shareholder in ANDE Corporation. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
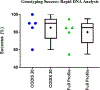
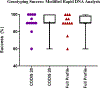




References
-
- Romsos EL, Vallone PM Rapid PCR of STR markers: Applications to human identification. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet 2015; 18:90–99. - PubMed
-
- Laurin N, Fregeau C Optimization and validation of a fast amplification protocol for AmpFlSTR Profiler Plus for rapid forensic human identification. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet 2012; 6:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Butts EL1, Vallone PM, Electrophoresis 2014; 35:3053–3061. - PubMed
-
- Giese H, Lam R, Selden RF, Tan E Fast Multiplexed Polymerase Chain Reaction for Conventional and Microfluidic Short Tandem Repeat Analysis. J. Forensic Sci 1998; 43:1287–1296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

