Principles of Electrophysiological Assessments for Movement Disorders
- PMID: 31986867
- PMCID: PMC6987526
- DOI: 10.14802/jmd.19064
Principles of Electrophysiological Assessments for Movement Disorders
Abstract
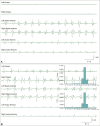
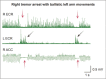
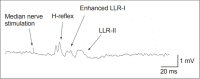
Electrophysiological studies can provide objective and quantifiable assessments of movement disorders. They are useful in the diagnosis of hyperkinetic movement disorders, particularly tremors and myoclonus. The most commonly used measures are surface electromyography (sEMG), electroencephalography (EEG) and accelerometry. Frequency and coherence analyses of sEMG signals may reveal the nature of tremors and the source of the tremors. The effects of voluntary tapping, ballistic movements and weighting of the limbs can help to distinguish between organic and functional tremors. The presence of Bereitschafts-potentials and beta-band desynchronization recorded by EEG before movement onset provide strong evidence for functional movement disorders. EMG burst durations, distributions and muscle recruitment orders may identify and classify myoclonus to cortical, subcortical or spinal origins and help in the diagnosis of functional myoclonus. Organic and functional cervical dystonia can potentially be distinguished by EMG power spectral analysis. Several reflex circuits, such as the long latency reflex, blink reflex and startle reflex, can be elicited with different types of external stimuli and are useful in the assessment of myoclonus, excessive startle and stiff person syndrome. However, limitations of the tests should be recognized, and the results should be interpreted together with clinical observations.
Keywords: Accelerometry; Dystonia; Electroencephalography; Electromyography; Electrophysiology; Myoclonus; Psychomotor disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mima T, Hallett M, Shibasaki H. Chapter 7. Coherence, cortico-muscular. In: Hallett M, editor. Handbook of Clinical Neurophysiology. Vol 1. Elsevier; 2003. pp. 87–94.
-
- Mauguière F. Chapter 5. Somatosensory evoked responses. In: Hallett M, editor. Handbook of Clinical Neurophysiology. Vol 1. Elsevier; 2003. pp. 45–75.
-
- Pratt H, Politoske D, Starr A. Mechanically and electrically evoked somatosensory potentials in humans: effects of stimulus presentation rate. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980;49:240–249. - PubMed
-
- Phielipp NM, Chen R. Chapter 10. Neurophysiologic assessment of movement disorders in humans, in movement disorders. In: LeDoux MS, editor. Movement disorders. 2nd ed. Boston: Academic Press; 2015. pp. 171–186.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

