Quantitative prediction of human pharmacokinetic responses to drugs via fluidically coupled vascularized organ chips
- PMID: 31988459
- PMCID: PMC8011576
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-019-0498-9
Quantitative prediction of human pharmacokinetic responses to drugs via fluidically coupled vascularized organ chips
Abstract
Analyses of drug pharmacokinetics (PKs) and pharmacodynamics (PDs) performed in animals are often not predictive of drug PKs and PDs in humans, and in vitro PK and PD modelling does not provide quantitative PK parameters. Here, we show that physiological PK modelling of first-pass drug absorption, metabolism and excretion in humans-using computationally scaled data from multiple fluidically linked two-channel organ chips-predicts PK parameters for orally administered nicotine (using gut, liver and kidney chips) and for intravenously injected cisplatin (using coupled bone marrow, liver and kidney chips). The chips are linked through sequential robotic liquid transfers of a common blood substitute by their endothelium-lined channels (as reported by Novak et al. in an associated Article) and share an arteriovenous fluid-mixing reservoir. We also show that predictions of cisplatin PDs match previously reported patient data. The quantitative in-vitro-to-in-vivo translation of PK and PD parameters and the prediction of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity through fluidically coupled organ chips may improve the design of drug-administration regimens for phase-I clinical trials.
Figures

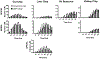
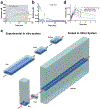
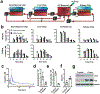
Comment in
-
Pharmacokinetic modelling using linked organ chips.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Apr;16(4):188. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0257-x. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32042110 No abstract available.
References
-
- Malinowski H et al. Draft guidance for industry extended-release solid oral dosage forms. Development, evaluation and application of in vitro-in vivo correlations. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 423, 269–288 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Danhof M, de Lange ECM, Della Pasqua OE, Ploeger BA & Voskuyl RA Mechanism-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) modeling in translational drug research. Trends Pharmacol. Sci 29, 186–191 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

