OPN binds alpha V integrin to promote endothelial progenitor cell incorporation into vasculature
- PMID: 31990676
- PMCID: PMC10792589
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-19-0358
OPN binds alpha V integrin to promote endothelial progenitor cell incorporation into vasculature
Abstract
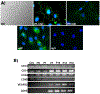
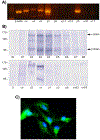
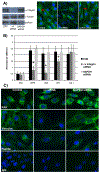
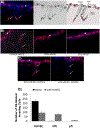
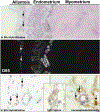
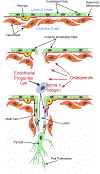
Angiogenesis is fundamental to the expansion of the placental vasculature during pregnancy. Integrins are associated with vascular formation; and osteopontin is a candidate ligand for integrins to promote angiogenesis. Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are released from bone marrow into the blood and incorporate into newly vascularized tissue where they differentiate into mature endothelium. Results of studies in women suggest that EPCs may play an important role in maintaining placental vascular integrity during pregnancy, although little is known about how EPCs are recruited to these tissues. Our goal was to determine the αv integrin mediated effects of osteopontin on EPC adhesion and incorporation into angiogenic vascular networks. EPCs were isolated from 6 h old piglets. RT-PCR revealed that EPCs initially had a monocyte-like phenotype in culture that became more endothelial-like with cell passage. Immunofluorescence microscopy confirmed that the EPCs express platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule, vascular endothelial cadherin, and von Willebrand factor. When EPCs were cultured on OPN-coated slides, the αv integrin subunit was observed in focal adhesions at the basal surface of EPCs. Silencing of αv integrin reduced EPC binding to OPN and focal adhesion assembly. In vitro siRNA knockdown in EPCs,demonstrated that OPN stimulates EPC incorporation into human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) networks via αv-containing integrins. Finally, in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry localized osteopontin near placental blood vessels. In summary, OPN binds the αv integrin subunit on EPCs to support EPC adhesion and increase EPC incorporation into angiogenic vascular networks.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest
There is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported. Greg Johnson is on the editorial board of Reproduction. Greg. Johnson was not involved in the review or editorial process for this paper, on which he/she is listed as an author.
Figures
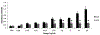

References
-
- Apparao KB, Illera MJ, Beyler SA, Olson GE, Osteen KG, Corjay MH, Boggess K & Lessey BA 2003. Regulated expression of osteopontin in the peri-implantation rabbit uterus. Biol Reprod 68:1484–1490. - PubMed
-
- Apte U, Banerjee B, McRee R, Wellberg E &Ramaiah S 2005. Role of Osteopontin in Hepatic Neutrophil Infiltration During Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207 25–38. - PubMed
-
- Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver M, Van DerZee R, Li T, Witxenbichler B, Schatteman G & Isner JM 1997. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 275 964–967. - PubMed
-
- Asahara T, Masuda H, Takahashi T, Kalka C, Pastore C, Silver M, Kearne M, Magner M & Isner JM 1999. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ Res 85 221–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

